1. Data and Information
Introduction
All Past Paper Questions: Click here
pg141
Data
Introduction
-
what
- just a collection of text, numbers and symbols
- with no meaning to it
- cannot be interpreted until it is organized
- data must have context to become information
- data cannot be interpreted until it has context
-
long description
- data on its own have no meaning
- data consists of raw facts and figures
- data can be in the form of characters, numbers, letters, signals, symbols, etc...
- when data is intepreted to have meaning, it's information
- for data --> information
- has to be processed
- needs to have a context
- information is what you get after a piece of data is processed & organized
-
context
- NOTE:
- "A possible context is that the data is about ###"
- "and the information we have might be ###, ###, ###, ###"
- example:
- NOTE:
Validation
-
why?
- cant gaurantee is data is accurate
- checking is data is sensible and follows rules
- checks if data entered is reasonable
- even if data is copied correctly
- it might be in an invalid format
- only "check digit" can check for transportation issues
- cant find transcription errors
- eg: format -> DOB should be as
nn/nn/nnnn(wherenis a real positive integer) - pickup invalid data
- cant pickup transposition errors, except for "Check Digit"
-
approaches
-
length check
- check how many characters long
- examples
- X characters long
-
range check
- check if data is given boundaries
- data must be lower than upper limit and greater than lower limit
- we should know the upper and lower limit
- examples
- between X and Y
- dates
- day: 1 -> 31
- month: 1 -> 12
- year: 1950 -> 2024 (assumptions)
- but will also allow dates like:
31/02/2001
-
check digit
- can only be done on long strings
-
lookup check
- be one of given values, like
typing.Literalin python.
- be one of given values, like
-
format check
- check if data is in correct format
- might not pickup transposition errors
- check if a string follows a certian pattern
- transposition errors will happen
- examples
- where
nis any real, positive integer - 8 numbers:
nnnnnnnn - dates
nn/nn/nnnn- but will also allow dates like:
69/96/3000(transposition errors)
- where
-
consistency check
- explain
- check if data have internal conflicts
- check if values are not in contradiction
- related data items can be checked for consistency of their relationship
- check fields to ensure the data in fields correspond to each other
- error message appears if error
- examples
- date of birth
- calculate age and check if it matches
- date of birth
- explain
-
type check
- check if data is of correct type: character, letter, or numbers
- this would not prevent accepting out of range numbers
- eg:
- no alpha to a numeric field
-
presence check
- make sure data is entered
-
-
examples
Verification
- why
- checks if data entered is copied accurately
- helps to stop users from making mistakes
- will pick up transportation errors
- will pick up transcription errors
- cant gaurantee is data is accurate
- can find transcription errors
- can only check data that is copied
- done by both human or by computer
- methods
- visual verification
- compare data being entered to another copy
- and check visually
- done by human against a source document
- printout of source document is used
- detected mistakes are corrected by the checker (human)
- unreliable: hard to deal with both paper and screen
- doesnt always identify all errors
- fast: data only needs to be entered once
- double data entry
- usually 2 people entering the same data
- each input compared against each other
- stored and matched by the computer
- it will alert if two inputs do not match and they can decide which version to keep
- data should be entered in exact order
- reliable: high chance of identifying errors
- but, if both people made the same error, big oof
- discrepencies (differences) highlighted as second copy is entered.
- parity check
- only when transferring data from computer to computer
- when data is transferred, computer counts the number of 1s in each byte
- each byte is checked individually
- if no. of 1s is even, parity bit is set to 0
- if no. of 1s is odd, pairty bit is set to 1
- (the goal is to have an even number of 1s)
- parity bits are sent along with data
- if number of 1s is odd after adding the parity byte, it means an error
- hash total
- a key number is calculated
- all account numbers would be added together
- to create a single number
- data is transmitted along with hash total
- hash total is recalculated once recieved
- original hash total is compared to the new one
- if they do not match, an error has occured
- the fields hold data ad will not be used with calculations
- visual verification
Test Data
- to text validation and verification
- types
- normal data
- within given range
- extreme data
- values at the border
- abnormal data
- not within given range
- normal data
- examples
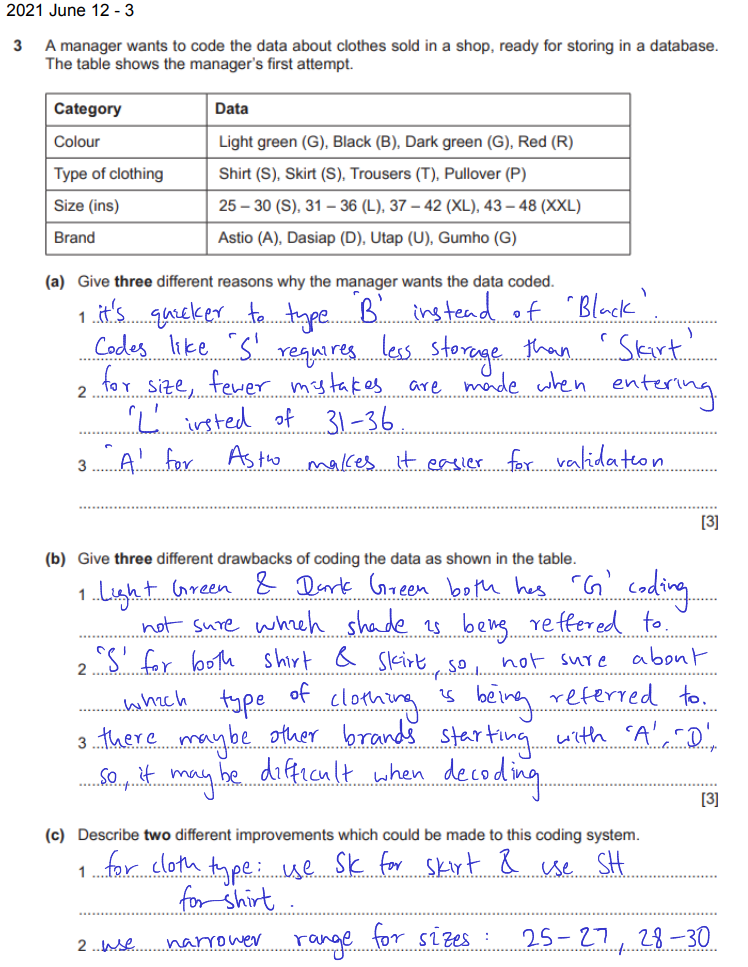
Coding
- advantages
- speed up data entry
- more accurate
- easy validation
- reduce length of data
- less space required
- small DB size = faster search
- disadvantages
- approximations is too general (for numerical values)
- hard to use in calculations
- coarserning of data
- several data starting with same letter
- eg: color
Bdoesnt tell if its light or dark - uncertain (obscure) about the meaning of data
- if codes are complicated, users might not enter correctly
- it is possible to run out of code combinations
- questions
Information
Types
- static information
- description
- sources are carefully checked for accuracy
- because they are hard to change once stored
- there is limited amount of information
- after creating, it cannot be changed
- examples
- news paper
- data that is unchanged is called static data
- news paper has data that cannot be changed
- as soon as news paper is printed, it cannot be changed
- newspaper's information must be checked thoroughly before publishing
- more reliable
- less errors
- since it cannot be updated, information in it becomes outdated quickly
- history assignments
- the history does not change
- so, once written and confirmed and printed, we dont need to add information
- news paper
- description
- dynamic information
- description
- information updated quickly
- so, usually upto date
- there can be many contributors
- eg: blog websites
- so, data is considered unreliable
- data that is read from and not written back to a file
- difficult to add information to static information source after it has been created
- can have many contributors, so, inaccurate
- eg: web page that is updated from time to time
- data's state is never expected to be the same when re-input
- eg: news websites, just when something new happens, the website is updated
- data's state is never expected to be the same when re-input
- description
- both
- need analysis techniques
- provides a mixture of both relevant and irrelevant information
Quality
-
description
- accuracy of collected information affects quality
- extremely high detail affects the quality of information somtimes
- irrelevant information affects quality
- more complete it is, better the quality
-
accuracy
- meaning
- information that is free from errors
- is true
- has been proven to be correct
- factors affecting
- info. must be accurate to be good quality
- if data is inaccurate, info produced will be inaccurate
- method of collection affects accuracy
- if questions asked arent phrased properly
- respondents will give inaccurate irrelevant responses
- if data entered is inaccurate, information will also be inaccurate
- meaning
-
relevance
- factors affecting
- relates to the situation
- information collected should be relevant to our need
- it should not concentrate only on one aspect of the problem
- it should not relate to different area of one being studied
- should not have too much information
- information should be complete to be useful
- if information is incomplete
- only some required information is present
- hard to solve problems using the data
- factors affecting
Age
- need to be kept upto dat
- might change very soon
- updating soon will increase accuracy
- bussinesses using out of date information might make bad decisions
- can use upto-date information for future planning
Level of details
- need correct level of information
- when solving company problems
- if too much information, hard to extract required info
- if less details, might not contain information we need
Knowledge
- points
- remebering a set of facts
- use of information to solve problems
- understanding that
25 = 5 x 5requires knowledge
- how information and knowledge are linked
- data consists of raw facts and figures
- does not have any meaning
- until its processed and given meaning
- information is data that is given meaning
- knowledge is know-how and learning contextualized information
- data consists of raw facts and figures
Data Collection
-
you only have to gather as much or as little data as you need
-
have full control over the method used to collect data
-
has an oppotunity to sell data
-
source of data is known exactly, making it easier to judge its reliability
-
examples
Direct Data Sources
- meaning
- data collected for specific purpose / task
- by many methods: questionairres, data logging, etc...
- gives data thats called "original source data"
- gives upto date information
- can gain qualitative and quantative data
- advantages
- full control of how data is gathers
- size of sample size can be as required
- ensures data collected is relevant to the study
- has an opportunity to sell the data
- source of data is exactly know, so, more reliable
- data is more utpo date
- diadvantages
- expensive
- need to hire people/company to gather data
- purchase equipment, like data loggers, printers, etc...
- comparatively expensive
- more time to gather data
- (by the time the project is completed, the data maybe outdated)
- small sample size
- less amount of data gathered
- might not be enough
- pollution, its affected by weather seaons...
- need clerks, (for data entry), more expensive
- expensive
- inaccurate information
- errors made when data entering
- misconfigured/uncalibrated sensors
- people used in study aren't very representative
- if question is not clear / badly phrased, we get irrelevant answers
- open ended questions will produce answers that aren't relevant
- maybe too much information when processing documents
- if MCQ, no enough choices for answers
- types
-
questionairres
- stuff
- distributed among people
- may affect accuracy
- people might not answer questions truthfully
- people may be biased
- questions maybe badly phrased
- cant expand on what the question means
- MCQs dont have sufficient number of answers
- possibility of people collecting data making errors
- disadvantages
- not taken seriously by people, ignored.
- stuff
-
interview
- stuff
- if question is not clear, we get irrelevant answers
- more time consuming
- as should interview everyone individually
- may affect accuracy
- can clarify the answer
- can ask questions based on previous answers
- includes open-ended questions
- so, its hard to quantify
- possibility of people collecting data making errors
- advantages
- ask questions based on previous answers
- can aks more in-depth follow up questions
- can interpret body language (eg: facial expressions)
- tends to be taken more seriously by people
- stuff
-
observation
- might be inaccurate
- people act different
- because they know that they are being monitored
- might be inaccurate
-
data logging
- description (short)
- sensors used to gather data that could be processed & interpreted
- description (long)
- automatic collection and storage of data
- using a computer and sensors to collect data
- this data is analyzed
- results are output in the form of graphs/charts
- data is collected over a period of time
- continuously at regular intervals
- analysis usually requires special software
- examples of physical variables that can be logged:
- temperature
- sound
- light
- pressure, etc...
- sound level monitor
- example: (in streets)
- more noise = more traffic
- less noise = less traffic
- example: (in streets)
- description (short)
-
Indirect Data Sources
- meaning
- data obtained from third party
- not necessarily related to our need
- data collected for a particular reason, other that what its being used for
- eg: population data can be collected from local government agencies
- could collect data from local environmental groups
- advantages
- can examine large set of data
- gather data from subject who we dont have physical access to
- large sample size
- more confidence
- low costs
- less time taken
- poorly written transcripts do not have to be read through to create data source by gatherer
- data already grouped and collated (grouped) into meaningful categories
- diadvantages
- data collected for a different purpose than the current use/research
- more time to filter unwanted information
- may have a sampling bias
- inconsistent codings used in different sources
- data is already coded, difficult to understand
- different data sources vary in reliablility
- depending on
- who collected the data
- how old is the data
- depending on
- may not be able to sell. it depends on the lisence.
- sources
- census data
- electoral register
- what
- list of adults who are entitled to vote in a national / national election
- readily available
- need to visit to city's council
- dont need to go from person to person collecting info
- data might be out of date
- address they live in
- people new to area aren't included
- new homes may have been built
- people may have died
- not all people who live at the same address are from the same family, eg: homestay
- what
- customers in stores provide personal information when they buy products
- a news paper
- encyclopedia
- medical records
- meauseum arhives
- example
- asking bussinesses for customer details to produce a mailing list
Data Processing
Batch Processing
-
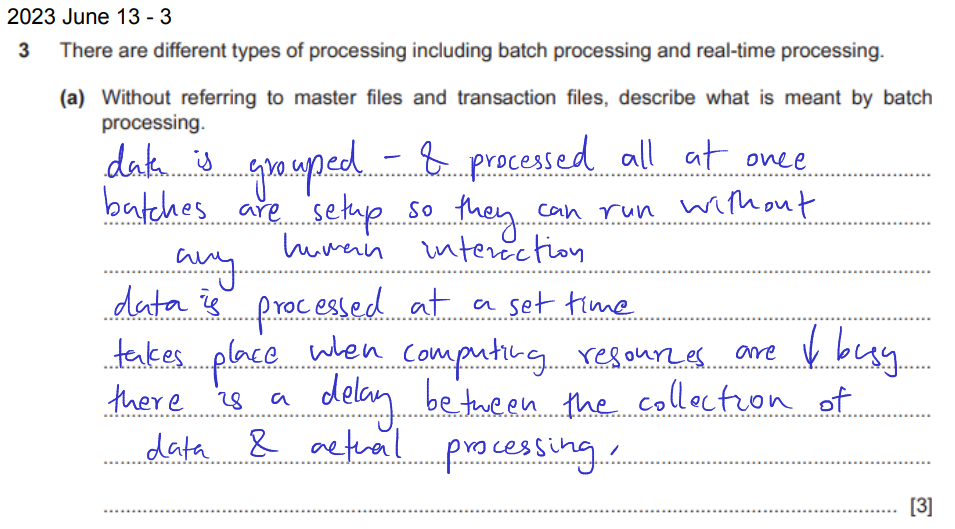
meaning (payroll)
- data is grouped and collected
- colecting data & processing it all at once
- jobs setup to run without human interaciton
- input data collected to batches & processed in whole
- data is processed at a set time
- batch processing happens when resources are less busy
- batches stored (queued) in work hours and run at night
- transaction file of input data is kept for later processing (hours worked)
- master files with employee details updated only monthly
- transaciton file used with master file to update master file at end of every month
- exmamples
-
advantages
- dont always need resources (but others might require)
- eg: payroll, runs only once a month / week
- but realtime processing happens all the time
- can be run in less busy time, eg: evening/night
- hours worked (in payroll) is known at the end of the day
- dont require immediate processing
- dont need more complex computers
-
disadvantages
- time delay in collecting input data
- information updates only after processing the transaction file
- system errors only revealed during processing (night)
- cannot toubleshoot until batch has finished processing
- admins cant stop processing until it ends after it starts
-
types of transactions
- Create (/Add) record
- eg: when a new worker joins the company
- Update (/Change/Amend) record
- eg: a worker changes department
- Delete (/Remove) record
- when a record is no longer needed
- eg: employee quits
- Create (/Add) record
-
uses
- in printing of electricity bills
- rocket scientists to moon
- used by payroll department to pay wages
- would be used if scientists had collected a very large amount of data offline & neeed to process all at once
- transaction file of hours worked is kept
- and used by master file to update the master file
- jobs setup to run without human intervention
- can use computer when its less busy
-
process (generic, detailed)
- before process happens
- transaction file is validated
- transaction file must be stored in the same order as master file
- how transaction file is used to update the master file?
- first record from transaction file is read
- first record from master file is read
- these two records are compared
- if they do not match
- computer writes master file record to new master file
- if it matches
- transaction is carried out
- computer does the calculation
- (tell what happens here)
- (examples)
- calculates the rate of pay: pay * no. of hours worked.
- (using rate from master file and hours worked from transaction file)
- processed record is written to new master file
- next record from transaction file is read
- and compared to the next reocrd of the master file
- and so on...
- this is done until last record of transaction file
- then, at last: all remaining old master file records are written to the new master file.
- before process happens
-
process (algorithm)
READ first record in transaction file
READ first record in master file
WHILE not end of transaction file
IF transaction file's record (ID) = master file's record (ID)
THEN
# processing
TotalPay <-- HoursWorked*RateOfPay
WRITE updated master file record
READ next record in transaction file
ENDIF
READ next record in master file
ENDWHILE -
examples
Realtime Processing
- stuff
- requires immediate processing
- ened more complex computers
- always upto date
- uses
- suitable for controlling a car park barrier
- rocket scientists to moon
- suitable for controlling rockets
- causes a response within specified time constraints
- (miliseconds latency - extremely fast)
- inputs are processed and affects the output
- which in turn affects the input
- controlling rockets often involve the use of sensors & control systems
- allows scientists to take immediate action
- if rocket goes off track, computer would immediately fire engines to correct in
- rocket guidance
- response time of computer is immediate
- responses are in order of miliseconds
- means that inputs are processed to produce and output
- which in turn affects the input
- processing for rocket guidance has to be continuous - should never end
- eg:
- if too much time is taken for the respone of the path
- rocket might collide with a rock in space
- for payroll (bad, unwanted)
- constant use of resources (which might be needed for other tasks)
- unncessary
- hours worked known only at end of day
- so, running at end of month/week is enough
- realtime processing does not involve processing of large volumes of data, such as running a whole companies payroll
Online processing
- data is processed as quickly as possible
- user is in direct communication with central CPU
- data is accurate and upto date all the time
- requires more hardware
- erros revealed immediately
- errors can be fixed immediately
Interative processing
- meaning
- computer deals with each input after short delay
- gives realtime responses
- delay is caused by the computer accepting the input
- delay is too small - users cannot even notice
- deals with one transaction at a time
- once completed, the database is updated immediatley
- booking systems acquires seat and updates it as booked
- sends a message to the user to inform that the seat has been blocked
- for ticket booking, why interactive processing instead of batch processing
- when DB is updated immediately, it wont overbook
- seats can be booked at any time of the day, day or night
- customers are able to retry to re-book if something went wrong the first time
Comparisons
- online processing vs batch processing
- online processing
- advantages
- orders processed right away
- completing orders can start sooner (no waiting)
- errors revealed immediately
- so, can fix quickly
- data is accurate and upto date all the time
- disadvantages
- high hardware requirements
- more expensive
- have to be active all day
- need workers at all time
- need more employees
- expensive salaries
- advantages
- batch processing
- advantages
- only limited number of workers to enter data
- only uses when nobody uses it
- eg: evening, night time
- processing does not slow the network down
- disadvantages
- if error
- reported after batch is completed
- delay in fixing
- if DB is interrogates
- can recieve results quickly
- why?
- sales invoices, customer queries bill
- BUT with online-systems, its available anytime
- more expensive
- more computer processing time required
- if error
- advantages
- online processing
Other
File Access
- sequential file access
- meaning
- records are accessed in order they were entered
- each record is read one by one
- until a match is found
- indexed sequential search
- index table would contain corresponding part of disk
- where names beginning with each letter of the alphebet are found
- for name beginning with Js, the part of a file containing records starting with As to Is can be ignored
- All records beginning with J will be read one by one until Johnson is found
- meaning
Proof Reading
- define
- slow and methodical search for errors
- careful reading and re-reading of a yet to be finally printed document
- to detect any errors & mark corrections for
- spelling errors
- typrographical errors
- grammatical errors, etc...
- checking different elements in the layout like
- headings
- illustrations
- colors, etc...
- also check for amitted words and endings
- how
- read carefully to find grammar/spelling mistakes
- print a hard copy and screen (instead of using a screen)
- read the essay out loud
- to hear problems
- that we may miss when reading
- check issues in similiar sounding words
- eg: its vs it's, their vs they're
- read backwards, sentence by sentence
- read forwards, to make sure subjects & verbs agree.
- use a blank paper to cover lines below
- to stop potentially skipping lines
Electronic Funds Transfer
- describe how
- chip is checked
- make sure its not marked as stolen
- is not expired
- is valid
- if error, show error
- PIN entered by customer is compared in PIN on chip
- if PIN is not verified
- error appears
- prompts user to re-enter the PIN
- upto 3 attempts
- if still fails
- reject the transaction
- if PIN is verified
- transaction continues
- computer connects to customer's bank to see if there's money
- if has money
- transaction is completed
- amount deducted from customer's bank account
- amount credited to supermarket's bank account
- if has no money
- insufficient funds
- transaction is rejected
- chip is checked
Online Store
- how to buy
- go to store website
- choose goods category
- select items to view more
- add to card if you like it
- at last, go to cart
- click on Buy Now
- proceed with the payment
- confirm billing address
- select payment method
- enter credit card information + OTP when it asks
- confirm the order
Charts
- Pie chart
- how to improve
- put labels pointing to sectors
- attach percentages to sectors
- attach number of X for each sector
- use different colors for each sector (to easily identify)
- have a chart legend
- eg: dashed lines files, dotted fill, solid fill, etc...
- disadvantage
- take more space
- hard to read
- as brain is bad at comparing angles
- more difficult as more segments & colors are added
- labels can be hard to fit, specialy to smaller segments
- how to improve
Other (other)
Coding (Other Types)
- encryption
- points
- scrambling of text in a message
- encoding so only authorized people can access them
- understood only if decrypted
- can only decrypt with key
- points
- codecs
- are hardware/software needed to convert data
- so it can be transmitted down communication lines