5. Expert Systems
All Past Paper Questions: https://docs.google.com/document/d/14POvsigutX83XWY9ESokphmqd_9j19Bf3Z7973Wkm_A/edit?usp=sharing
Expert Systems

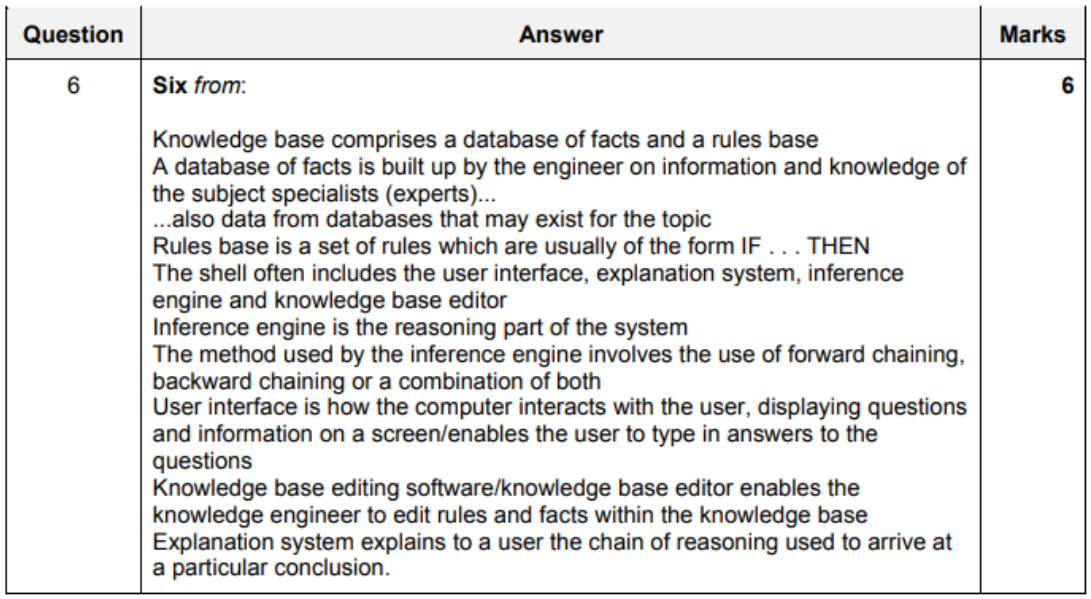
- Components of an Expert System
- knowledge base
- has a database of facts and rules base
- facts is built up by the engineer
- on information and knowledge of the subject specialists
- also from database that may exist for topic
- rules base if a set of rules in the form: 'IF...THEN'
- shell includes
- user interface
- explanation system
- explains the user
- the chain of reasoning
- used to arrive at a particular order
- explains the user
- inference engine
- knowledge base editor
- enables knowledge engineer to edit rules and facts
- of the knowledge base
- enables knowledge engineer to edit rules and facts
- inference engine does the reasoning
- uses forward chaining
- backward chaining
- or both
- user interface is how the computer interacts with the user
- displaying questions
- information on screens
- enables user to type in answers
- knowledge base
Uses
-
general answer
- UI asks questions (about illness)
- patient types in symptoms
- rules base is a set of rules
- the inference engine
- uses data/facts from knowledge base
- is able to find possible diagnoses
- by using a form of reasoning
- uses forward reasoning or backwards chaining or both
- compares symptoms to whats in knowledge base
- uses rules base of 'IF...THEN'
- knowledge base editor
- enables knowledge enginner to edit
- possible diagnoses output to user-interface
- explanation system
- produces reasons for suggestions
- and outputs to user-interface
-
scheduling system to route vehicles
- store locations of each distribution point
- store type of vehicles being used
- store working hours
- scheduler would type in destinations
- system would match those against available types of vehicle
- match against locations
- suggest how many drivers would be needed
- suggest vehicle needed for each driver
- suggests allocation of orders to each vehicle
- ?? suggest list of goods in reverse order ??
- ?? so that, each vehicle had the first order loaded on to the vehicle last ??
- system would take into account the fuel and time
- outputs the most efficient rule
User Interface
- used for both input and output
- how computer interacts with the user
- description
- allows user to enter problems
- questions output by system
- allows user to input answers to questions
- further questions are output to the UI
- based on previous answers
- outputs suggestions of possible solutions
- and explanation of findings
Techinician
- Enters data using an interactive user interface
- questions based would be asked from techinician
- answers are entered to questions
- techinician would see probabilities of diagnoses output from the system
Knowledge base
- comprises of database of facts
- and a rules base
- built up by the engineer on information
- knowledge of subject specialists
- description
- holds database of facts
- that the interface engine searches
- contains rules base
- which consists of 'IF...THEN' constructs
Knowledge base editing software
- enabled the knowledge engineer to edit rules and facts
- of the knowledge base
Knowledge engineer
- employeed to create an expert system
- responsible for maintaining the system
- edits facts in knowledge base
- edits rules in rules base part of knowledge base
- deleted unused rules from the rules base
Rules base
- set of rules
- in the form: 'IF...THEN'
Inference Engine
- reasoning part of the system
- description
- compares data to whats held in knowledge base
- uses rules base, in the form of 'IF...THEN'
- produces suggestions
- uses explanation system to produce explanations
- as how to solutions were arrived at
Forward Chaining

![]()

- starts with available data
- uses inferenece rules to extract more data
- until a goal is reached
- use is to search the inference rules
- until it finds a rule
- then, uses the 'THEN' part
- to cause addition of new information
- rejects any rule that is not true
- this is iterated repeatedly
- until a goal is reached
- this is 'data-driven'
Backward Chaining
- starts with a list of goals
- and works backwards
- would search inference rules
- until it finds one
- which has a 'THEN' part that matches a desired goal
- if the IF part of the rule is not false,
- then it is added to the list of goals
- this is 'goal-driven'
- because list of goals determines which rules are selected and used
Explanation system
- explains to a user the chain of reasoning
- used to arrive at a particular conclusion