2. Hardware and Software
All Past Paper Questions: https://docs.google.com/document/d/1AjL53GAhZXb_fa4mALsTHMoJZlIfAlF35uHH96iPWQ4/edit?usp=sharing
Computers
-
fault tolerance
- both
- whether computer will repair itself if an error occurs
- a computer can operate even if components fail
- without system downtime
- computers operating quality can be reduce
- but it does not fail completely
- whether when a hardware component fails, is it hot swappable
- super computer only
- will run two copies of software
- if one fails, the second copy will start
- both
-
heat maintainance
- computers generate a lot of heat
- due to quality and quantity of processors
- it can be a problem when it overheats
- to address this issue
- good cooling systems are needed
- can air cool with an AC - expensive
- can water cool - cheap, efficient
- build datacenter in a cold part of the world, eg: greenland.
- good cooling systems are needed
- computers generate a lot of heat
Mainframe Computers
-
description
- have hundreds of processor cores
- all cores share one OS
- mainframes use parallel processing
- can process a large number of small tasks at same time
-
advantages
- have faster processing
- can perform hunders of MIPS
- have high value of MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures)
- so, less downtime
- have greater fault tolerance
- can transfer processing from one core to another
- so, hardware and software updrades can occur while the system is still running
- they can run different OS
- so, can handle different types of database
- they are more secure than most other types of computer
- as they use complex encryption system
- have faster processing
-
disadvantages
- very expensive to buy
- some are using cloud instead of this
- due to this being too expensive
- maintainance
- cost to people who manage this
- software costs
- cooling costs
- need large rooms
- generates a lot of heat,
- need good, expensive and complex cooling systems
- very expensive to buy
-
why used to produce census?
- mainframes has a,
- high speed of processing data
- scalable
- reliable
- amount of data to be processed is very large
- as countries have a lot of people
- it also keeps on increasing
- census processes & produces more data
- more poweful machines are needed as more data is added
- mainframes has a,
-
transcation processing systems
- performance is meausured by the number of transactions it can process in a given period of time
- must be continously available
- must able to maintain integrity of data
- and overcome hardware and software problems
- it must also be possible to individually upgrade hardware and software components without suhtting down the system
- there should be controlled access, allowing only authorised users to use the system
-
performance metrics
- used to measure performance speeds of computers/processors
- can be unreliable as the complexity of instructions can vary according to which benchmark program is used
- MIPS are used for integers
- Million Instruction Per Second
- measured in millions
- used when measuring performance of computers involved in running application software
- do not take into account the input/output speeds
-
RAS
- Reliability, Accessibility and Serviceability
- describes the robustness/durability of a mainframe computer
- Realiability
- chance of the system behaving as intended
- Accessibility
- mainframe being operational at all times
- Serviceability
- can be easily fixed within a short period of time
- if there is a failiure
- reliable
- will use alternative methods to carry out tasks
- software is reliable
- highly tested
- and updates are made quickly to fix problems
- MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures) is long for mainframes
- mainframes give months/years of systemd owntimes
- when unavailable (due to failiure)
- mainframe is unavailable for a very short time
- spare components (CPUs) are inlcuded in mainframes
- if one fails, nother takes over
- mainfram can determine why failiure occured
- enables hardware and software components to be replaced without affecting mainframe's operations
- can be serviced while the system is still running
Super Computers
-
description
- can have more than 100,000 processing cores
- use massively parallel computing
- each core has it's own OS
- use more than one GPU
-
effectiveness / features
- have a limited lifespan of just a few years
- and will need replacing / repairing
- carries out complex calculations
- can use complex maths formulae
- can handle a large amount of items of data at same time
- fasted data processing computers
- most expensive to buy
- each processor has it's own operating system
- use massively parallel processing
- more powerful compared to mainframes
- can be upto 1000 times faster
- can include scientific rules
- some tasks do not require super computers
- overheats, hard to keep it cool
- as the task is not complex, so, it would be a waste of time
-
performance metrics
- used to measure performance speeds of computers/processors
- can be unreliable as the complexity of instructions can vary according to which benchmark program is used
- (M) FLOPS are used for real/floating point numbers
- Floating Point Operations Per Second
- measured in quadrillions and higher
- used where complex (scientific) calculations need to be carried out
- to not take into accuont the CPU's clock speed, bus speed and RAM available
-
weather forecasting
- powerful enough to carry calculations required
- can process huge amounts of data
- based on use of very complex/scientific computer models
- a advanced three-dimentional model of earth has to be created
- and large number of complex calculations are carried
- but first, data should be collected
- records of previous weather conditions
- weather measurements from weather stations
- observations from satellites
- information from ships & aircrafts
- records of previous weather conditions
-
climate research
- many variables are collected
- using sensors, eg:
- rainfall, temperature, humidity, etc...
- using sensors, eg:
- large quantity of data is processed
- complex calculations are carried out
- shows historical trends of different variables over a long time period
- complex maths formulae are used to describe how different parts of climate works
- computer models based on these are used to predict how the climate will change
- these models will include several scientific formulae
- model will give you the best guess
- many variables are collected
Cloud Computing
- cloud storage
- advantages
- paying a low monthly fee
- has no physical precense, so, takes no space
- can backup data automatically
- syncing ensure files are automatically updates across all devices connected
- disadvantages
- data is in hands of third party
- so, less secure
- providers can be transient
- resulting in possible data loss
- only as reliable as the user's internet connection
- some may charge a cheap initial fee, but may increase prices later
- users are at risk of not having data stored in compliance with government regulations if the physical storage location resides in a different country
- data is in hands of third party
- advantages
Software
- Software are programs used to direct the operation of a computer and related hardware
FULL DIRAGRAM IMAGE HERE
System Software
-
directly operates the computer hardware
-
both compiler and interpreter converts high level programming language to a lower level instructions
-
designed to run a computers hardware and application programs
-
managed computer hardware
-
provides a platform the application software to run
-
general purpose
-
takes care of memmory management of the system
-
Question


Compilers
-
features
- translates the whole porgram as one complete unit
- creates an executable file
- is able to report on a number of errors in the code after compilation
- does not need to be present in order to run the program (compiled executable)
- can optimize source code to run as fast or as efficiently as possible
- often produces a seperate object code program
- converts high level instructions to machine language
- entire file is compiled before execution
- list of errors is created after the compiltation process
- compiled program is directly executed using the machine code
- has to be recompiled even if the smallest change is made
- difficult for hackers to modify compiled code
-
advantages
- once compiled, translation software is no longer needed
- runs faster (fast execution)
- quicker process than interpreting
- improve security for programmers
- making it harder to copy code
- fewer risks of copyright infringement
-
disadvantages
- can only be used in one OS
- target audience may run many OS
- might need to use an interpreter
- has to be recompiled even if the smallest change is made
- can only be used in one OS
-
usually, compiles with native compiler
-
to run in another platform
- can cross compile
- will run more slowly
- produces more errors and mistakes
Interpreters
-
how it works?
- translates each line of source code inito an intermediate stage and then executes that line / statment
- translation happens line by line (one instruction at a time)
- reports on errors as lines of source code are processed
- an interpreter has to be resident in memmory in order for the program to run
- only a few lines of the program need to be in memory
-
features
- translates each line of source code inito an intermediate stage and then executes that line / statment
- reports on errors as lines of source code are enetered
- only a few lines of source code needs to be in memory at any one time
- some interpreters execute code within a virtual machine
- these have been designed to disallow code from directly accessing the data computer
- converts high level instructions to an intermediate form (called "object code")
- translates one statment at a time
- stops translating after the first error
- interpreter has to be in memmory for the program to run
- can be modified at runtime (changing functions)
-
advantages
- when need to run on many OS
- can maintain one version of the source code
- less time will be spent on maintainance
- when updates are needed
- easier to debug the program
- as errors are highlighted
- it can use up less memory than a compiler
- as only a few lines of source code are in memory at given time
- less likely to crash the computer
- as the code can run in a virtual machine (like JVM for java)
- when need to run on many OS
-
disadvantages
- translation software may need to be kept upto date
- interpreted programs run slower than compiled programs
- as they have to be interpreted every time they are run
- interpreting a program is much slow process than compiling
- as it stpos every time an error is encountered
- source code is easier to convert by fraudulent users
- makes it much easier to copy the program
Linkers
-
a linker takes one more more object files and combines them into a single executable file
-
advantages
- programs can be written in modules
- requires less RAM
- saving cost of memmory
- whole program and compiler dont need to be in memory at the same time
- requires less RAM
- saving cost of memmory
- several programmers can work on seperate modules
- saves time (compared to one person writing the whole code)
- if there is an error, only that module has to be fixed
- programs can be written in modules
-
disadvantages
- variable names can cause problems
- the same variable may have been given different variable names in different modules
- documentation has to be more detailed
- so takes longer to write
- variable names can cause problems
All
- why we need all of these?
- many programming languages allow the wiritng of different peices of modules seperately
- programming tasks are simplified as large programs can be broken into smaller manageable pieces
- the linker is used to put all the modules together
- without the comiler, the linker would have no object files to combine
Operating systems
-
tasks carried out / purpose
- allocates memmory to software
- sends instructions to printers
- recognizes and responds to input devices
- opens and closes files on devices
- does file management
- multi-programming systems allocate equitable processing time to each task
- sends error messages if an error
- hanldes user logins
- handles file permissions
- provides the interface between a user and the computer
- manages hardware resources
- responsible for handling errors
-
purpose
- multi-processing OS is when system has more than one processor
- multi-tasking OS allows more than one program to run at a same time
- multi-tasking OS allocates sufficient processor time to each program
- multi-threading OS allows different parts of a single program (process) to run at the same time
- real-time OS allo the computer to respond to input instantaneously
- distributed OS allows data to be stored on a number of computers in different locations
Device drivers
- purpose
- it controls a device attatched to the computer
- without required device driver, corresponding hardware device fails to work
- it is the interface between OS and hardware device
- tells the OS how to communicate with hardware device
- upon installation, it detects and identifies peripheral devices
- handles translation of requests between device and computer
- ?? defines where outgoing data must be stored before it can be sent ??
- different OS may send different instructions, driver translates them to what printer can understand
Utility Software
- programs that help maintain the computer
- performs a very specific task, usually, managing system resources
- OS can contain a number of these utilities out of the box
- why it is needed?
- to keep computer free from viruses
- to make files contiguous
- ?? needed to improce performance by allocating memmory ??
Anti Virus Software
- note: viruses are also a type of software
- to remove viruses
- scans computer for viruses
- software used to prevent, detect and remove malicious software (called 'malware' for short)
- can protect from:
- malicious browser helper objects,
- browser hijackers,
- ransomware,
- keyloggers,
- backdoors,
- rootkits,
- trojan horses,
- worms,
- adware,
- spyware,
- etc...
- signature based detection
- compares the contents of file
- to its database of known signatures
- heuristic-based detection
- detects malware vased on characteristics typically used in known malware code
- behavourial based detection
- based on behavourial fingerprint of the malware at runtime
- is only able to detect malware after they have start malicous actions
- sandbox detection
- based on behavourial detection
- but it doesnt detect behavourial at runtime
- it executes the programs in a virtual environment
- logging the actions performed by the file
- gives the user options to delete or qurantine the files
- does backgroudns cans of downloads and attatchements
- prompt the user to scan newly plugged in
Data Compression
- to reduce storage file size of a file
- encoding information using fewer bits than the original representation
- two types
- lossless compression
- reduces the number of bits
- by identifying repeated patterns
- and encoding them in special ways
- eg: Run Length Encoding (RLE), Huffman Encoding
- same quality
- information is not lost
- reduces the number of bits
- lossy compression
- reduces the number of bits
- by identifying unncecessary information
- and removing them
- reduced quality
- information is lost
- reduces the number of bits
- lossless compression
Disk Defragmentation
- removes non-contiguous spaces on disk
- organizes contents of the disk into smallest number of contiguous blocks
- it is re-arranging the files stored on the disk
- attempts to create larger regions of free space using compaction
- some defragmentation utilities try to keep smaller files within a single directory together
- the movement of the hard drive's read/write heads over different areas of the disk when accessing fragmented files is slower
- compared to accessing the entire contents of a non-fragmented file sequentially
- will make the data retrieval easier and quicker
Disk Formatting
- prepares a data storage device for initial use
- organizes the tracks on a disk into sectors
- a new disk medium is fully prepared in order to store files
- the first stage is low-level formatting followed by
- partitioning which makes the data storage device visible to an OS
- followed by high-level formatting which generated a new file system
- low-level formatting divides disk surface into tradcks, secors and cylinders
- done by magnetising disk areas using write heads
- tracks are numbered s tarting from 0
- when the head goes from one treack to next, it leaves a gap
- each track is organized into numbered sectors, starting at 1 and seperated by gaps
- the purpose of low level formatting is to prepare the disk surface to reveive data
- high level formatting
- creates a file system on the disk
- this allows the OS to use the disk space to store data and access files
Backup Software
- to make copies for future use
- creates additional copies of all data in the computer
- backed up data is available incase of data loss, eg:
- lost to a ransomware
- accidental deletion
- can use copies to restore original contents
- asks use to enter type of backup
- full
- incremental
- differential
- etc...
- can backup automatically, on scheduled time, set by user
- backup process will consume disk resources
- making the computer slow
- so, should make backup at convenient time
- eg: night time
- taking backups regularly
- will prevent the chance of data loss
- asks if you wish to restore the backup
- asks if you wish to verify the backups
- asks frequency of backups (how often they should take place)
- ask which medium the user wishes to store
- select where to save the backup
- target location
- it should be secure
- can also encrypt the backup
- provides more security
File Copying
- creation of new files, which has the same contents as an existing file
Deleting Files
- removing a file from the computer's file system
- most OS keeps track of where files are on hard disk using pointers
- each file and folder on a hard disk has a pointer that tells the OS
- where the file's data ends and begins with
- when a file is deleted,
- OS deletes pointers
- marks secotrs containing that file as available
- its considered that files are no longer present in hard disk (considered as free space)
- uses a file allocation table (FAT) to store the location of files on the disk
- the delete utility just deletes the reference of the index in the FAT
- until OS writes new data, deleted files are still recoverable
- recovery programs can scan for deleted files and restore them
- if file is partially overwritten, can only recovery half of that file
- file recovery pointers work by reinstating pointers
- reinstating the index in FAT
Application Software
- group of software designed for the end user
- uses computer to perform specific tasks
- not required to run the system
- its user specific
- interface between user and system software
- eg: spread sheet software, word processing software, database software, animation software, video editing software, etc...
Word Processing Software
Spreadsheet Software
- Click here to learn more
More Stuff
-
word processing software vs spreadsheet software
- similarities
- allows users to enter numeric and text data into a report
- can perform calculations using formulae and functions
- let users format text with fonts, colors, etc...
- allow importing of graphics like images and charts
- includes ability to save files in many formats
- have spelling and grammar checking
- has search and replace functions
- have page formatting options, headers, footers, etc...
- differences
- text alignment and page margins are handled in different ways
- spreadsheet
- users can create models
- create "what is" scenarios
- uses cells, rows and columns to hold data
- users can create models
- word processing
- can produce reports & mail merge
- only has basic functions to aid calculations
- doesnt restrict where data can be entered (no cells)
- includes word count feature
- similarities
-
cross application support (why cannot import word file to spreadsheet file)?
- word processing files are word processing file type
- spreadsheets are a different type of files
- to overcome issues,
- convert word processing file to generic file format
- save word processed file as .txt or .csv
- then, he will be able to open it
Off the Shelf Software
-
description
- software that is ready-made and already exists
- it is available to all bussiness and companies
- it is owned by a company that created it
- has to adapted to fit the bussiness that has purchased it
-
advantages
- cheaper, as mass produced
- available straight away
- testing can be righteously carried out by developers, so, less bugs
- many sources of support
- web forums
- comminity support
- wiki's
- includes helplines with operators who have already dealth with many problems, so, experienced
- will have been used many times before companies buy it, so any bugs will have been identified/reported and fixed
-
disadvnatages
- difficult to adapt to particular use required by the school
- has bloated, distracting, unwanted extra features
- may not be compatible with current systems and infrastructure
- some very specific functions may not be available
Custom Written Software
-
description
- software that is specially developed for a specific company
- it is made to accomodate that customer's particular preferences and needs
- written by programmers to solve specific problems
- owned by the bussiness that commisions it
- is it made from scratch
-
what
- software created for defined purposes
- does not need to be adapted for use
- any built in settings can be changed
- programmer will ensure device compatibility
- if software doesnt meet companies requirements
- programmers with have everything fixed
- eg: ability to copy software to several devices
- they will not have unncecessary bloated features
- the usually takes less space than off the shelf software
- so, less expensive storage costs
- the usually takes less space than off the shelf software
- company will own the custom written software, so, they can sell it to others
-
advantages
- designed specifically for client's requirements
- there will be no unncessecary features
- it does not have to be adapter for use
- programmers are available to make any changes required
- programmers will ensure the software is compatible with company devices and infrastructure
-
disadvantages
- costs more to pay programmers to write more
- testing is limited to only what programmers think is required
- based on how they think the software will be used
- not thoroughly tested
- so, can have a lot of bugs
- support is limited to team of programmers only
- can take a long time to develop the software
Mental Model
-
explanation?
- based on bliefs, not facts
- what user will describe as what they need
- deisgner must produce UI to match user's thoughts
- model of what users know/think about a system
- users create mental models very quickly (even before using any software)
- comes from prior experience of user
- designers should stick with this, or it will be hard for users
- user will take less time to learn (if product is similar to his mental model)
- will provide the user with transferrable skills
- training can be changed to fit user's mental model
- to fit the design of the interface
-
advantages
- easier for user to use UI
- takes less time to learn how to use the UI
- interface is predictable as it will match their requirements
- user will gain transferrable skills
- so, easier to use other apps
-
disadvantages
- range of definitions of what constitutes a mental model
- can cause confusion
- resulting in inaccurate results
- lack of clear methodology to use
- leading to a bias
- based on designers own intepretation
- little research
- maybe difficult to match user interface to user's perception of real world
- range of definitions of what constitutes a mental model
Conceptual Model
- actual model that is given to the user
- through the user interface
- of the product
User Interface
- What to consider when creating a custom user interface?
- how color is to be used
- (color palettes)
- choosing color combinations
- layout
- positioning elements
- to ensure readability
- increase font size to emphasize importance of certain elements
- only display information the user needs
- decide which controls will be required
- which navigational aids are required
- navigation bar (top)
- side bar
- breadcrumb
- how color is to be used
User Interfaces
-
CLI & GUI
- more accurate & reliable
- user must be sitting infront and controlling it
- require actions to deliberate
-
GBI & Dialog Interface
- for handicapped users (physical disabilities) who cannot use keyboard and mouse
- or control their limbs accurately
- more expensive to develop
- for reasons of hygene, not even a doctor is allowed to touch the device
- then, use gestures or dialog to control device
- not suitable for safety related stuff
- if in emergency
- (GBI) gesture might not get registered
- (DI) 'stop' like words might not be identified properly
- if in emergency
- for handicapped users (physical disabilities) who cannot use keyboard and mouse
CLI
-
Command Line Interface
-
prompt appears in screen
-
after which the command is typed
-
used by advanced computer users
-
less likely to change over time
-
uses less memmory
-
requires user to learn many commands
-
processing is faster than others
-
doesnt require graphics or high-resolution monitor
-
disadvantages
- user should learn many commands
- can be slowed to input, for new users
- long lines of text needs to be entered, instead of a few mouse clicks
- commands can be more difficult to edit
- more difficult to multi task
- very basic, and can be more of a strain to user's vision
- more likely to make mistakes when typing commands
GUI
- Graphical User Interface
- involves the use of WIMP
- Windows, Icons, Menus, Pointers
- layout
- sensible use of white space
- information that needs attending to immediately should always be displayed in prominent position
- a consistent use of screens
- must not overload the user with information
- should follow the house style of the company using it
- information should flow in a logical order to the user
Dialog Interface
- Dialog Interface
- stuff?
- requires a microphone
- can speak into a microphone to control the device
- requires training session with user
- unreliable when there is a background noise
- gives hands free control
- can use when driving, can use voice instead of driving with one hand
GBI
- Gesture-Based Interface
- stuff?
- can perform a gesture to control the device
- quicker way of initating a response from a device
- less effective when several users or with background movement
- gestures can be taught through manuals
- unreliable when used in the dark
- bad when driving, will have to drive with one hand while doing gestures with the other hand
- unintentional gestures might be registered
- very reliable as most users have similar gestures for communicating
- requires a line of sight (unlike dialog interface)
Hardware
- Another name for physical parts of the computer
- collection of physical components
CPU
-
parts
- Arithmetic Logical Unit (ALU)
- Control Unit (CU)
- Memmory
- tends to be contains on an intergrated circuit chip called a microprocessor
-
function
- CU fetched instrctions from main memmory
- decodes instructions
- executes instructions
- all input data are transferred via CPU's memmory
- memmory stores instrctions as well as data
- data is stored in the CPU memory, whilst a calculation or instruction is being carried out
- input data are transferred to the ALU for processing
- ALU makes use of 4 basic functions: +, -, *, /
- ALU uses certian logic operations such as comparisons, selections and matching
Mother Board
- description
- the main printer circuit board of a computer
- connects the main components of a computer
- contains
- mass storage interfaces
- serial and parallel ports
- usb ports
- network ports
- expansion slots (PCI, PCIe)
- controllers required to control standard peripheral devices
- southbridge
- connections for attatching additional boards
- bios
- CPU socket
- RAM slots
Sound Card
- description
- manipultate and output audio
- manipulate sounds stored on disk
- recieve sound from input from a microphone
- output sound trhought speakers connected to the bord
- nearly all sound cards upport MIDI, a standard for represeting audio electronically
Input Devices
-
Touch Pad
- used to simulate the behvaiour of a mouse when using a laptop
-
Keyboard
- or 'number pad' - whats used in supermarkets
- type in values
- advantages
- experiences users can enter data more quickly
- disadvantages
- difficulty of entering amounts other than selecing numbers using a mouse
- data is slow to enter (compared with DDE)
- using the keyboard
- can use CTRL + other keys to save, print, copy, paste, cut, etc... (keyboard shortcut)
- can use arrow keys to navitage through text
- can use tab key to indent, delete key to delete forwards, backspace to delete backwards
- can use the alphbetic keys and number keys to type content
- in a shop, if product bar code is damaged, it cannot be input
-
Touch Screen
- both input and an output device
- could be used to eneter amounts
- quicker to enter data than using a mouse
- may cause screen to be stained and make viewing difficult
-
RFID reader
- reader can be used to enter details from passport / bank card
- quicker than manually entering data
- readers are expensive to buy initially
-
in Bank Cards (credit cards / debit cards)
- uses a chip reader to read cards
- reliable than reading a magnetic stripe
- quicker than typing details from the card
- contactless card readers speed up transactions as no PIN is required
- in many countries, there is a maximum amount of money allowed to be charged with this.
- chip and pin-reader
- reads details from bank cards
- more secure
- more reliable than rading magnetic stripe
- quicker than typing details from the card
-
Bar Code Scanner
- used to read bar codes from products
Output Devices
IMAGE HIERARCHIAL
-
Monitor
- results are produces instantly
- graphs / diagrams / figures are represented more accurately
- scroll through results easily (instead of turning pages)
- need to be infront of monitor to view the output
-
Printers
-
easier to annotate printouts taken
-
printouts can be transported and viewed anywhere
-
may skim on whats on-screen.
- so, more likely for errors to occur
-
Dot Matrix Printer
-
not very clear comparatively
-
uses continous stationery
-
slow to print
- if busy, will cause queues of people waiting to print
-
less risk of this running out of paper
-
will have 'noise' in print (bad)
-
cheaper to run
- ink ribbon is cheaper than catridges or toners
-
advantages
- can use carbon copy paper (requires less filling of the sheet feeder)
- could use continuous stationary
- which would require less human interction
- doesnt run out of paper very quckly
- ink ribbon lasts longer and is cheap
- when ink runs out, print gets fainter, but is still legible
-
disadvnatages
- striking of heads cause a lot of noise
- distracting in office envrionments
- quality of output is not very good
- 240dpi, but inkjet does 1200dpi
- slow output
- to buy a dot matrix printer is very expensive
- has a more limited character set
- striking of heads cause a lot of noise
-
-
Inkjet Printer
- high quality tickets
- slow to print
- (all copies, including the first copy)
- if busy, will cause queues of people waiting to print
- will need to change catridges more frequently
- when ink runs out, prinout is less legible
-
Laser Printer
- quiality of print will be good
- can see it clearly
- takes time to produce the first copy
- does not have tio change toner as often as inkject catridges
- quiality of print will be good
-
Storage Devices
- Exam Question:


Primary
-
quicker than secondary
-
ROM content is sometimes copied to RAM and subsequently read from RAM
-
very fast access times
-
no moving parts
-
stores data in use and stores data for later user
-
RAM
- Random Access Memmory
- stored information for short term usage
- volatile: data is deleted once power is lost
- stores active program data
- ?? faster than ROMs ??
- used by computers for storing data during computing processes
- stores active program data
- can both read and write
-
ROM
- Read Only Memmory
- cannot be changed, only read
- non volatile: data is retained even when power is off
- stores permanent computer instructions
- (to store bootup instructions) contains instructions for the computer to start up when it is turned on again
- stores bootup instrctions - that will activate the hard disk
- to store software that is unlikely to need frequent updates
Secondary
IMAGE HIERARCHIAL
-
portable
-
non volatile
-
stores data for later use
-
CPU can both read from and write to data
-
Optical Drive
- uses laser to burn dark pits into medium
- each dark pit is a binary digit
- if there is a pit: 1, else: 0
- Advantages
- faster data access times (comapred to tape)
- more viable when theres large variations of temperature
- Disadvantages
- not very portable (compared to tape)
- more suspectible to damage when handling
- types:
- CD
- DVD
- stored upto 8.7GB max (DVD - Double Side - Double Layer)
- Blu Ray Disk
- single blu-ray stores upto 128GB max
- can store high quality videos
- more expensive
- costs less to buy per unit memmory
- single blu-ray stores upto 128GB max
- note:
- BR drives can read DVDs
- DVD drives cannot read BR dicsts
-
Magnetic Media
- aka Tape
- small areas of tape are magnetized to represent 1/0
- have surfaces coated with magnetically sensitive material such as iron oxide
- Advantages
- costs less per unit storage
- so, more cost effective (for large companies)
- stores more data
- appropriate for server backups
- less suspectible to damage when handling
- because its completely encased
- hardest to hack into
- costs less per unit storage
- Disadvantages
- costs more per tape
- gets curropt if placed near a magnetic field
- slower access speed
- as data is stored sequentially
- when getting data, should start at beginning and start finding
- not very silent
- it also has moving parts
-
Hard Disk Drives (HDDs)
-
have surfaces coated with magnetically sensitive material such as iron oxide
-
Advantages
- higher storage capacitie
- cost less per gigabyte
- lasts longer
-
Disadvantages
- consists of various moving parts
- more suspectible to damage and shock / more prone to failiure
- more pront to mechanical failiure
- access speed is limited
- depends on how close the data is to the read/write heads
- loud, have whirring sounds due to moving parts
- high power consumption
- consists of various moving parts
-
How it works? & Parts:
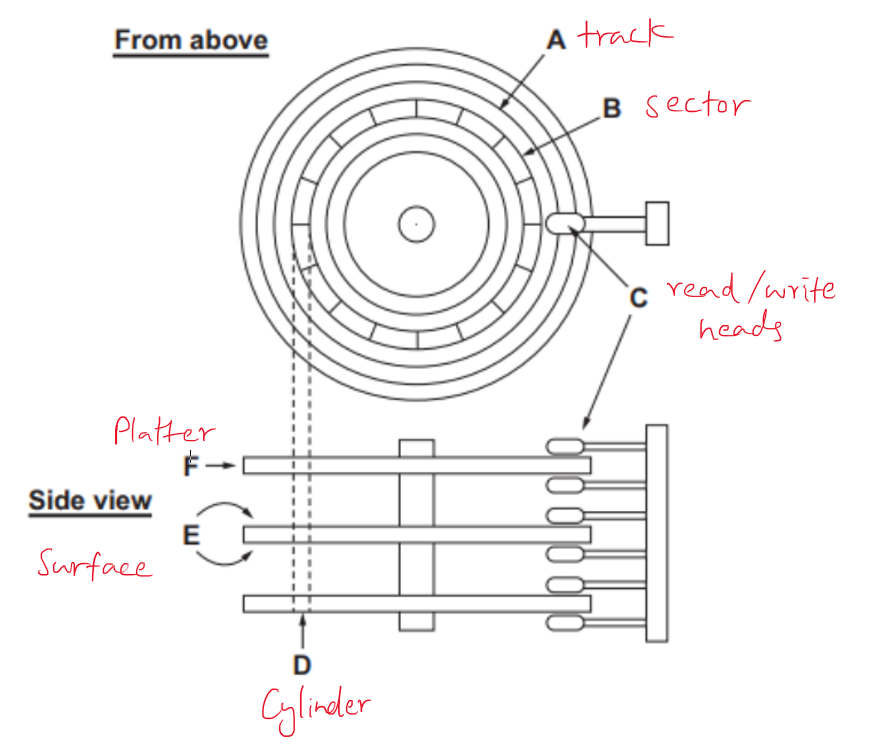
- HDDs consists of several platters, which are individual disks
- each surface of a platter has it's own read/write head
- the read/write heads move across the platters
- stoppping only read data from or write data to the surface
- it never touches the surface
- each surface is divided into several tracks, which are in the same position on each disk
- the track on the top platter together with the tracks exactly below it, form a cylinder
- each track is divided into sectors
-
-
Solid State Drives (SSDs)
- uses electric circuits (NAND flash)
- stores data with an electrical charge
- Advantages
- have faster transfer rate
- have quicker boot ups
- can have almost instantaneous data access ()
- all parts of SSD can be accessed at once
- use less power at peak load
- energy efficiency can deliver longer battery life in laptops
- no moving parts, so, SSDs run silently
- data can be accessed at once (specially thanks to the DRAM cache)
- Disadvantages
- low storage capacities
- costs more per gigabyte
- doesn't last long
- NAND flash used in SSDs can only be used for a finite number of writes
- choices and availability is limited
-
HDDs vs SSDs
| Feature | HDD | SSD |
|---|---|---|
| Storage Capacity | Higher storage capacities | Lower storage capacities |
| Cost per Gigabyte | Costs less per gigabyte | Costs more per gigabyte |
| Durability | Lasts longer | Doesn't last as long |
| Shock Resistance | More susceptible to damage and shock | No moving parts, so more shock-resistant |
| Access Speed | Limited access speed | Faster transfer rate, quicker boot ups |
| Noise | Loud, with whirring sounds | Runs silently |
| Power Consumption | Higher power consumption | Uses less power at peak load |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower energy efficiency | Better energy efficiency, longer battery life |
| Availability | Widely available with more choices | Limited choices and availability |
| Lifespan | Consists of various moving parts | Finite number of writes due to NAND flash |
- Pen Drives
- used to store data that is to be transferred
- from one computer to another
- because of ease of portability
- used to store data that is to be transferred
Other
- Pg 39 - 2019 March 12 - 1 (to Database)
Software Stuff (to Database)
-
NOTE: THIS BELONGS TO THE 'DATABASE' PART OF P1
-
generic file format
- description
- one which will be recognizable to most software packages
- if a software packages does not recognize, file is update to load
- examples
- .txt (text): can be loaded by most word processing software
- .csv (command seperated values): can be loaded by most spreadsheet software
- description
- a text file
- with data (including empty data)
- seperated by a delimiter
- a comma/',' is the default delimiter
- why used by spreadsheet software?
- smaller in size
- so, less processing time
- can be opened by many applications
- data can be exchanged easily
- among different spreadsheet software
- among different computers & operating systems
- its human readbale
- easier to edit manually
- description
- why use text file instead of using word processed file?
- file size is smaller
- takes less storage space
- so, has small processing time
- text format doesnt need to buy license / software
- eg: of word processing software
- can be opened by more applications
- data can be exchanged among different OS / Computers
- word processing software has many versions
- one may not support documents made with another verison
- its human readable and easy to edit manually
- disadvantages
- no distinction between text and numeric values
- documents will have no formatting
- cant embed images / graphics / videos
- cannot have tables
- resulting layout may make it difficult to read
- file size is smaller
- description
-
propietrary software
- software that is owned by an individual or a company (usually the one that developed it)
- there are almost always major restrictions on its use
- a software vendor delineates the specific terms of use in an end-user license agreement
- its source code is almost always kept secret
- usually covered by copyright which provides a legal basis for its owner to establish exclusive rights
- usually created by a company
- with secret (proprietary) encoding scheme
- so, it can be decoded only using software of company
-
open source file formats
- description
- can be used and implemented by anyone
- an open source file format can be used by both propietrary and FOSS
- also called free file formats if they are not covered by any copyrights
- so that anyone may use them at no monetary cost for any desired purpose
- can be opened by most types of software
- there is a published speicifcation for storing digital data,
- usually maintained by a standards organization
- can sometimes be amended without violating of copyright laws
- provides a standard file type
- can work with different software without the need to have the same software
- why need this
- not everyone can afford proprietary software
- when transferring from one device to another,
- other devices may not have compatible software
- archived proprietary files maybe difficult to read by new software
- description
Web Conference (to Digital Divide)
-
NOTE: THIS BELONGS TO THE 'DIGITAL DIVIDE' PART OF P1
-
how to setup
- answer 1
- send emails to every person being invited informing them of the conference
- he sends log in details to users
- uploads any necessary documents for the meeting
- sends a link to the website
- enter his username and password (obtained from the provider)
- select a start time and end time
- in the meeting area, type an agenda
- using the software select participants
- select appropriate meeting space/room
- select those participants who can enter the room
- choose those who can be presenters
- and who can manage the meeting
- limit participation of participants,
- disable messaging,
- disable camers
- answer 2
- setup equipment and software
- agree a date and time
- send reminder to participants before they start
- send invitation link, with meeting password
- adjust webcam so that can be seen
- create and enter virtual rooms
- share documents with appropriate software
- upload any necessary documents for the meeting
- sends a link to the website
- enter his username and password
- using the software, select participants to accept in to the meeting
- select appropriate meeting space/room
- select those who can enter the room
- limit the participation of participants, mute, disable messaging / camera, etc...
- communicate by speaking into a microphone and looking at the webcam
- answer 1
-
hardware required
- server to handle video conferencing software
- laptops/devices for each participant
- microphone to speak to (sound - input)
- speakers to hear (sound - output)
- large monitor to see all participants
- cameras/webcams to input pictures
- router to connect to internet / network
Web Authoring (no idea yet)
- using web authoring software instead of html?
- advantages
- do not have to spend time learning html
- do not need to have web development knowledge/skills to make a functional website
- can make websites with basic clicking and typing
- writing html takes much longer
- most are WYSIWYG editors
- disadvantage
- limits the users options as a designer
- they only rely on templates with limited options
- depening on what web authoring software package you use
- they might not even different features
- software may make user reliant to it
- if software breaks, can no longer develop the site
- learning html means sites can be built from any environment with basic text editing software
- eg: notepad (most basic) to intelliJ webstorm ide (advanced)
- advantages
Encryption (to Security)
-
NOTE: THIS BELONGS TO THE 'SECURITY' PART OF P1
-
how encryption stores data stores on a hard disk?
- can use either symmetric or asymmetric encryption
- can be through the use of public and private keys
- causes data to be scrambled
- requires an encryption key to encrypt
- requires a descryption key to decrypt
- resusls in data which is not understandable
- even if read by someone else, it will have no meaning
Inference Systems (to Expert Systems)
-
NOTE: THIS BELONGS TO THE 'EXPERT SYSTEMS' PART OF P1
-
how inputs are used to prodice diagnoses
- finds possible diagnoses by using a form of reasoning
- the inference engine uses the data or facts in knowledge base (to reason through the symptoms)
- the reasoning involves forward chaining, backward chaining, or a combination of both
- compares symptoms to those in the knowledge base
- uses the rules base of IF...THEN... rules
- also, write the description of forward chaining and backward chaining