10. Animation
All Past Paper Questions: https://docs.google.com/document/d/1osDm8ZWYpGqo4qsB4ioe_5NMqt8prnXxOrlloWsXQ6c/edit?usp=sharing
Audio
- bit-rate
- changing bit-rate
- Audio quality improves with increasing bit rate
- 800 bit/s is minimum for speech to be recognised
- 32 kbit/s — generally acceptable only for speech
- 96 kbit/s — generally used for speech/low-quality streaming
- 128 or 160 kbit/s — mid-range bit rate quality
- 192 kbit/s — a commonly used high-quality bit rate
- 320 kbit/s — highest bit rate level supported by the MP3 standard
- lossy compression to reduce bit rate can introduce artefacts
- caused by data/quantisation errors
- distortion of sound
- perceived/heard as 'bubbling'
- stuttering/jerky/silences in sound.
- Audio quality improves with increasing bit rate
- changing bit-rate
Computer Animations
Key Frames
-
why
- to define start and end of movement of an object
- to specify movement of objects
- that the viewer will see
- to define timing of movement
- by position of key frame in sequence of frame
-
property key frames
- defines (one or more) properties of an object in a frame
- (Objects properties)
- can be edited (within a property key frame)
- to create in-between (tween) frames without the need to draw each frame individually
- used as 'roving' (property key frames)
- ensures speed of motion is consistent between frames
- (throughout a tween)
- to adjust the speed of motion
- at beginning and end of tween sequence so that it appears more realistic between frames/throughout a tween
- to add properties of one object onto other
- by copying property key frames in timelines
- defines (one or more) properties of an object in a frame
-
how sequence of frames created
-
question 1
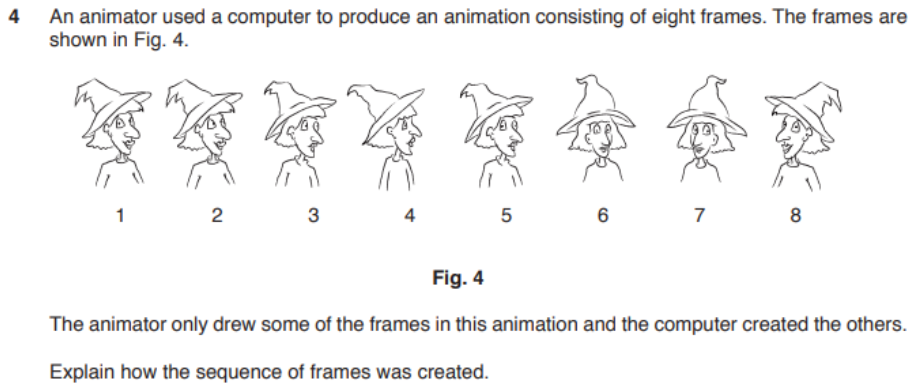
- answer
- Animator drew frames 1 and 5 and 8
- Frame 8 created by flipping frame 1
- These are used as key frames
- Frame 1 was duplicated to create frames 2, 3 and 4
- Frame 5 was duplicated to create frames 6 and 7
- Key frames define the start and end point of transitions that can be used by a computer-based animation application
- Tweening was used to create frames in between.
-
question 2
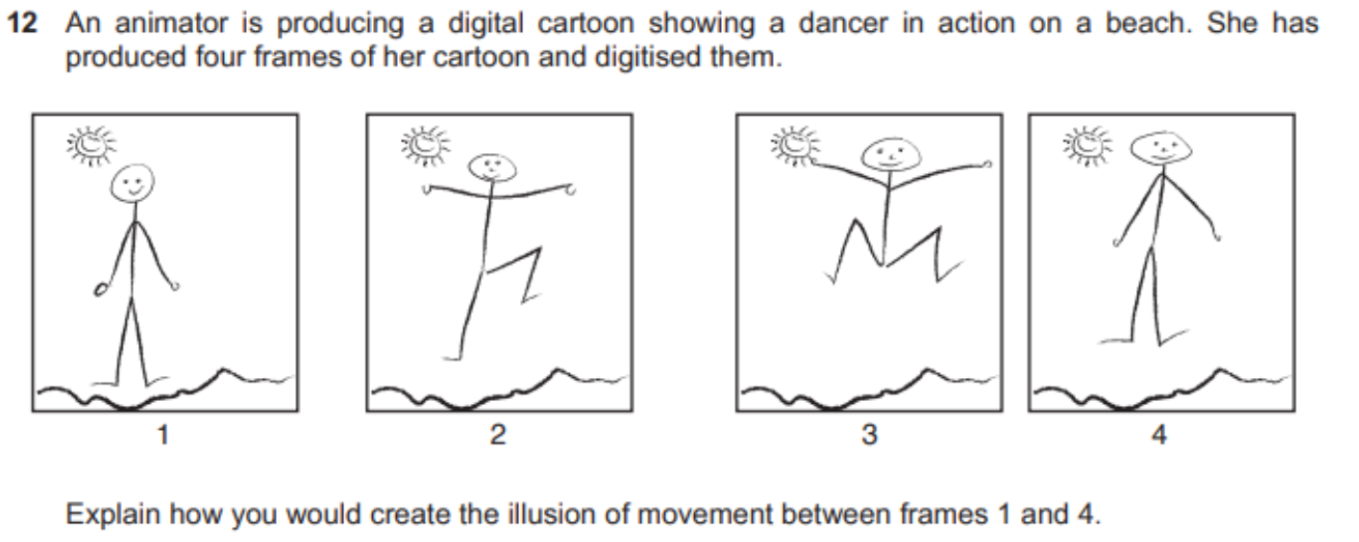
- answer
- Using the four frames as key frames
- filling in of frames between frames 1, 2, 3 and 4
- using variable frame frequency depending on content
- fewer frames between frames 1 and 2 than e.g. between 2 and 3
- as background is stationary then lower frame rate than foreground characters
- May be low frame rate so makes motion jerky (+ unrealistic)
- Need to add at least 8 frames in order to create smooth movement
- Need to add enough frames so that frame rate is below 'flicker fusion' threshold
- else movement will appear to flicker and illusion of movement is destroyed
- Motion blurring of the figures between frames 1 and 2 etc.
- can simulate faster movement.
- Using the four frames as key frames
-
Editing
-
call animation
- Background objects drawn on one cell and placed at bottom of stack of cells
- Character to be moved drawn on transparent cell
- placed on top of background and photographed
- Character redrawn as moved (on transparent cell) and replaced
- Re-photographed/digitised in next frame
- Process repeated for subsequent frames.
-
stop motion
- Scene arranged and lighted
- Camera app setup
- Frame recorded
- Frame checked for corrections
- Frame deleted if not required
- objects moved slightly and re-photographed into new frame
- Use of 'onion-skinning'
- faint outline of previous frame in app
- to show placement of objects
- Frames duplicated
- to slow the motion down
- e.g. when character changes direction suddenly.
-
text animation
- strokes
- an outline around the text letters
- animated to move around the letters
- to fade in/out around the letters
- to different formats/colours e.g. dotted/dashed/thickness
- to different comer formats e.g. sharp/smooth/rounded
- fill settings
- changes the contents of the letter shapes
- Change the colour of the letter/shape
- gradients
- types
- (multicolour) colour gradients gradually change one colour into another
- linear gradients change colour along a single axis (horizontal or vertical)
- radial gradients change colour in an outwardfinward direction starting from/to a central focal point
- direction/focal point of gradient can be changed.
- types
- strokes
Animations
Properties
-
orientation
- description 1
- is a camera property that is set in a keyframe
- Surface sets the target for the camera on the object surface
- Provides a sense of gravity for the object
- Space sets the target for the camera at the centre of the object.
- description 2
- Sets the x, y, and z rotation angles around a fixed point (the origin) in a layer
- (Rotation) around the x-axis is the roll, yaw, angle.
- (Rotation) around the y-axis is the inclination, pitch, angle.
- (Rotation) around the z-axis is the azimuth, heading, angle.
- description 1
-
transparency
- (Sets the visibility of the objects, so) other layers in the display can be seen underneath.
- Can be set to different percentages (of transparency/opacity) to change the visibility of layers underneath
- Adjusted in keyframes to affect following frames
- Can be adjusted so that some colours are removed screen effects
- Can set a 'transparency track' in keyframes so transparency/opacity percentage changes between keyframes.
-
animation speed (in 24fps)
- usually 24fps or 30fps
- each frame
- actions may need to be very active / fast
- animation can include a flurry of acitivity
- around the main object
- can make very smooth animations
- each two frames
- animator only needs to draw on 12 fps, not 24fps
- saves time
- less animators needed
- cheap
- makes slow animations smoother to eye
- less accuracy required
- (than drawing on each frame)
- animations appear more lively / active
- animator only needs to draw on 12 fps, not 24fps
- each four frames
- animation may appear jerky
- flashing of objects (on/off)
- objects move very fast
Techniques
- tweening
- stuff
- usues location points
- changes motion by creating intermeddiate frame
- requires establishment of keyframes
- moves points of location of object to new points
- morphing doesn't do it
- stuff
- morphing
- stuff
- changes one object into different object
- smooth
- overlays grid on images & uses it to remap new image
- stuff
- tweening vs morphing
- similarities
- can change shape of an object
- motion of object
- can change size / color / location
- similarities
Dimentions
-
2D objects
- drawn in 2 dimensional space
- measured in 2 axes/height and width/H x W/X and Y axes
- based on (concept of) frames//
- appear flat
- cannot appear to rotate through 360 degrees
- are only viewed from one/front angle
- are only lit from one/front angle
- lack texture/solidity
- cannot/are not realistic in live scenes
- examples
- use in social media sites
- presentations
-
3D objects
- in 3 dimensional space
- measured in 3 axes/height, width and depth/H x W x D/X,Y and Z axes
- can have (appearance of) volume/depth
- based on (concept of) movement (of objects)
- have (appearance of) rotating through 360 degrees
- (appear to) be viewed from different camera angles
- (appear to) be lit from different directions
- (appear to) have texture/solidity
- (appear to) be placed into live scenes/elements with more realistic appearance
- examples
- use in movies
- cartoons
- video games
Other
- image editing, when making movies
- Add visual special effects/CGI (computer-generated imagery)
- to video sequences
- show stuff that cannot exist in reality
- Colourising monochrome film stock to increase acceptability
- Images can be improved
- eg: color grading Images can remove/include objects Images of impossible objects/situations can be created Altering photographic images to enhance
- sales of products (can mislead buyers)
- appearance (can mislead fans)
- Add visual special effects/CGI (computer-generated imagery)