9. Graphics
All Past Paper Questions: https://docs.google.com/document/d/1Wx551YT0F35Ca0DI4uQ0bNIO0xf0-jFKEjCNY9tOkkE/edit?usp=sharing
Questions left out:
- p3-ch11-pg64
Bitmap Images
- how its stored
- Made up of pixels
- Each pixel represented by bits
- 1 to 64 bits per pixel
- Number of pixels depending on colour depth
- Bits representing pixels packed in rows for bmp
- Rows rounded to 32 bit words
- Padding needed for loading into memory locations
- (Usually) stored from bottom left up to top right of image.
Compression
- why
- reduce file size
- use less storage
- faster file transmission
- emails
- loading web pages
- low image resolution for small screens
- glitch art can make use lossy compression artefacts to alter images
- JPEG (lossy) might have artefacts
- reduce file size
Lossy Compression
-
how (1)
- Images are reduced in quality
- Information is lost forever
- cannot be restored
- algorithm removes areas with low detail more than areas of high detail
- so image is changed from original
- compression artefacts may appear
- Image quality reduced with repeated compression
- because at each compression, more image information is lost
-
analysis / how (2)
- Loss of image data
- has visible effect
- image quality is reduced
- Compression artefacts
- produced during compression
- can be visible
- so, reduce image quality
- Sudden changes in colour in an image can cause rings near the edges
- Conversion of a gradation in tone by loss of data into fewer tones causes posterisation
- False edges created
- contouring
- because reduction of grey levels
- Loss of data in curves
- low quality due to
- low colour depth
- Reduction in resolution
- might can mistake text in images and change the meaning
- e.g. 6 mistaken for 8.
- Loss of image data
-
justify the use (of lossy compression)
- (basically the same thing as above)
- reduces data needed to represent images (& reconstruct)
- reduces file size
- can store more images in same disk space
- can transfer files quickly
- reduced load time
- better user experience
- can attacth to emails, without exceeding file sizes
- can post on social media (optimized)
- comprehension artifacts can be used by artists to enhance visual impacts on images
Lossless Compression
- description
- no information is lost
- Image is recreated with no difference from the original
- Works well with images with blocks of similar pixels
- because only need to store data for one pixel and number of pixels
- No loss of quality
- algorithms can reconstuct original pixels lost by compression
Editing
Editing Techniques
- editing techniques
- Cropping of images to remove unwanted areas
- use of rule of thirds to keep image visual balance
- can lose important detail if poorly used
- Colour balance adjustment to change 'feel' of image
- whiter to create warm mood
- bluer to create cooler feel
- restore natural colour to flesh tones
- Brightness changes to change of image
- increase in contrast for photos taken on dull days can show more detail
- decrease in contrast for photos taken in bright sun can increase detail in shadows
- replacing an object in the image
- combining elements of different photos to create a new photo.
- covering part of the image with another object
- Creating a digital illustration (of original photo)
- Changing to a different background
- Create an illusion of depth
- Create special effects
- Adjusting the image itself
- change the transparency of an image
- resizing of photos
- reducing noise in the image
- correcting lens distortion/perspective.
- Cropping of images to remove unwanted areas
Editing Tools
-
morphing (sad face -> happy face)
- Uses forward mapping of pixels from one image into next
- sad face mapped to new position in smiling face
- Setting of control points in start image to map exactly to points in final image
- Pixels in start image mapped to points in final image that are determined by 'weighting'
- Gaussian function in software
- Pixels next to control point move more than those further away/
- less than control points
- Pixels further away from control point are less affected by software algorithm so move less.
-
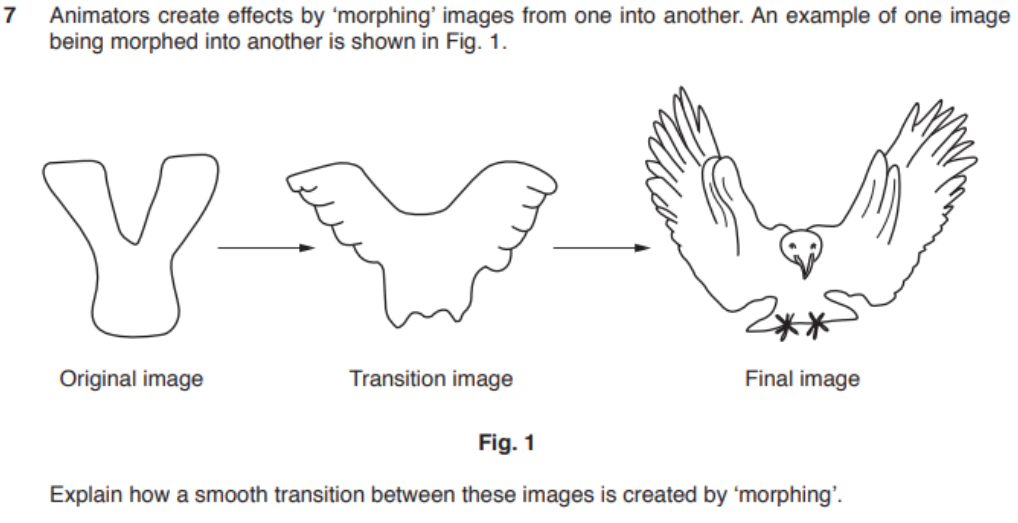
morphing (bird flying)
- question
- answer
- Warping (deforming) from the original images so final image has same shape
- use of forward mapping
- each pixel in original image is mapped to an appropriate
- pixel in final image
- use of reverse mapping
- each pixel in the final image is sampled for an usable pixel in the original
- all final image pixels are mapped to an original image pixel
- Cross-dissolving the images
- a sequence of images shows a gradual fade from one to the other
- via a (series of) transition images
- original image is gradually distorted and faded out
- final image starts out totally warped to the first and is faded in.
- Warping (deforming) from the original images so final image has same shape
- question
Editing Tools - Examples
-
question 1

- answer
- Photographs opened in image editor
- Person image cut out from photograph 1
- Mask around person is created to cover background
- Selection to be cut is highlighted/drawn
- Selection is modified around edges to ensure accuracy
- Using of adjustable nib for drawing tool
- Cut unwanted parts of image of woman
- Background of cut image changed to transparent
- Copy cut out (to clipboard)
- Create new layer for image of woman
- Import/paste cut out into image of office/photograph of office/Fig. 10.2
- Place new image in correct
- Resize image of woman (as required to fit in image of office)
- Bring to front/back as necessary
- Flatten/merge layers (if required)
- Correct new image for overlap/misplaced parts/pixels of imported image
- Crop area of new image/photograph 2 as required.
-
question 2

- answer
- Removal of Private barrier structure:
- Freehand selection tool to select structure
- Cut tool to remove object from the image
- Colour picker tool to select background behind barrier
- Paint tool to fill in area where barrier removed
- "content aware fill" or use the spot healing brush tool
- blend backgrounds where
- select and copy and paste to disguise where shadow of barrier was on path
- Addition of new lamp post:
- Freehand select tool to select lamp post
- Copy tools to copy lamp post to clipboard (leaving existing in place)
- paste new lamp post into new layer
- Position new lamp post as required
- Clean up pasted image:
- Colour picker tool to select colour to be painted into edges of added image
- paint tool used to fill pixels around image to make it 'blend' in
- Use of appropriate brush size
- Adding text for title:
- Create new layers for text and path
- Type text and create path for the text
- Use text to path to create shaped text
- Position text
- Remove temporary layers
- (used to construct title)
- Finalising image:
- Merge layers to 'flatten' image.
- Removal of Private barrier structure:
-
question 3

- answer
- Perspective tool has been used (to correct perspective)
- by 'stretching' the image across the top
- to align the sides of the stores
- Rotate right tool used to an building infrotn
- Curtains (in left windows)
- inserted by copy & paste
- using right-hand set (as source)
- cropped to remove some building
- resized to improve aspect ratio.
- Perspective tool has been used (to correct perspective)
-
question 4
- part 1
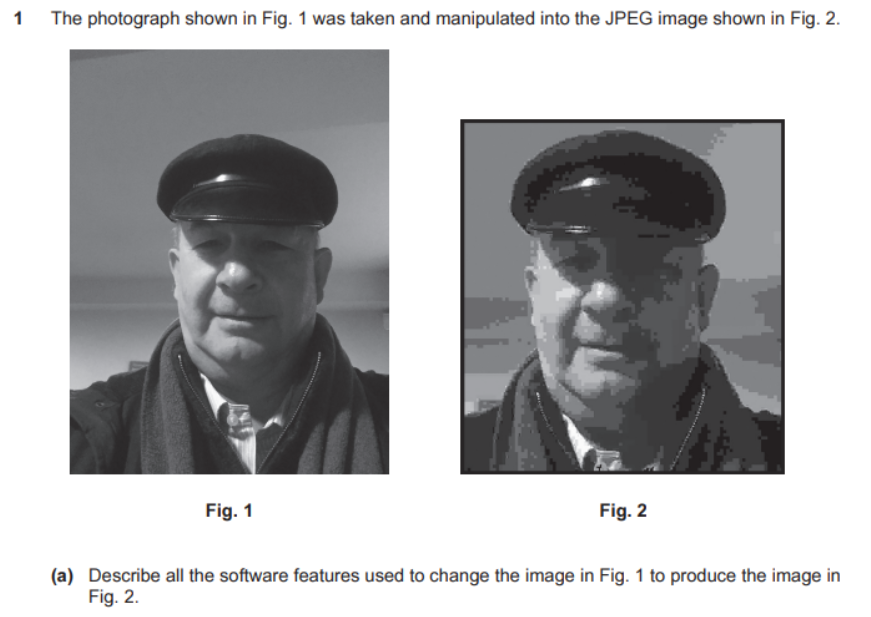

- answer
- Crop tool to show the face only
- Border line added to the whole image
- Resize tool to make image larger
- Saved as compressed (JPEG) format
- part 2

- answer
- both 1 & 2 - are saved as a bitmap
- Bitmaps are made of pixels
- 2 - is a compressed image with too much compression
- Loss of pixels
- details in face are lost
- compression artefacts visible to the human eye
- 2 - large to be seen by human eye
- When enlarged, it becomes more visible
- The face now looks unrealistic(/blocky)
- part 1
-
question 5
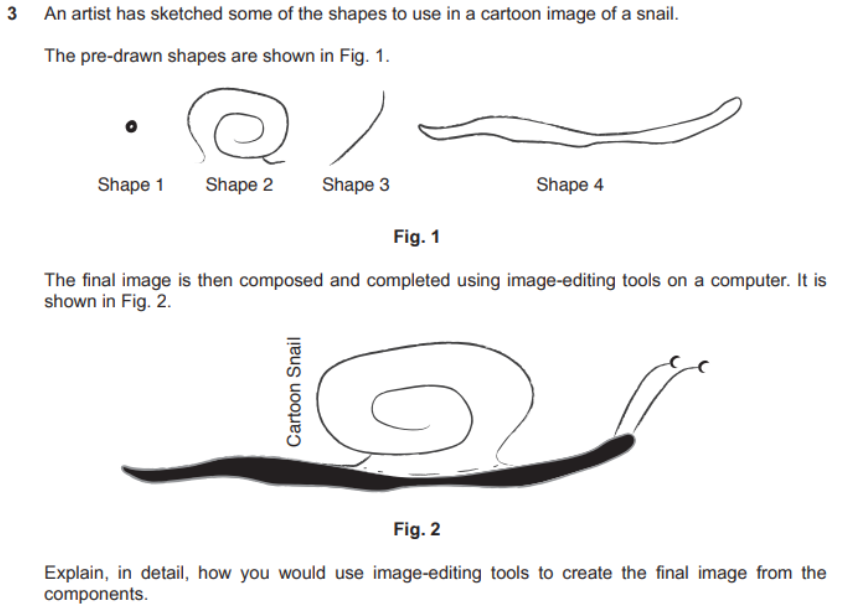
- answer
- reate new canvas/image on whic to compose the na imageo e sna
- Copy and paste/scan all components into the new canvas so that they are ready for editing
- Ensure that all backgrounds of all shapes are set to transparent to allow overlap of
- Shape 1 has part of the image cut out/erased to produce the eye shape
- Shape 1 is copied and pasted to produce two images for the eyes of the snail
- Shape 2 is inverted/fiipped horizontally (across the vertical plane) and resized larger/enlarged for the shell
- Shape 3 is rotated by 90 degrees and inverted horizontally to form one of the antennae
- resulting shape is copied and pasted and stretched horizontally to form the second antenna
- Shape 4 is resized, filled with black to form the body of the snail
- All the shapes are positioned/aligned together/grouped to form the composite cartoon snail
- Brush tool with size is used to ensure that the join between shape 2/shell and shape 31body is complete/no gaps are left
- used to add dotted line at base of shell/shape 2
- Text is added and rotated left by 90/right by 270 degrees
- text is positioned as shown
- Conwnents are grouped and resized together to form final image.
Impacts of Editing
-
politics
- fake news
- altering photos
- adding peopl to unrelated places
- to make people beleive he participated
- removing people
- to make them beleive he did not participate
- retouching images
- to make them more attractive
- viewers unaware if image if manipulated
- fake news
-
fashion magazines
- enhance appearance of items/models
- attract attention of viewer
- to compensate for
- reduction in attention span (in recent years)
- make poor photos appear neat
- (to increase sales)
- cheap than taking perfect photos
- making models look nice
- Removing blemishes, wrinkles, flabby parts
- altering body shape
- A unrealistic body image (is created)
- models can lower viewers self-esteem
- cause eating disorders
- cause unnecessary pressure
- to confirm to unrealistic ideals
- takes time
- so, slows down production
Uses
-
photography (website)
- use thumbnails of large image to show photograph
- terms
- bitmaps
- made of pixels
- created from existing pixel data
- stored in an array in memmory
- thumbnail
- are smaller verions
- to load/display quickly
- contain links to larger versions of same file
- are smaller verions
- bitmaps
- evaluvation
- Pixel values may be modified individually
- Photographic quality achieved by increasing the data about each pixel
- or number of pixels
- (in vectors, whole image must change)
- use compression to reduce file size
- Bitmap files translate well (eg: when printing)
- large file size, when large no. of colors
- techniques to view image quickly
- Data compression
- introduce artefacts that 'spoil' images
- slow down the reading
- (decompression should happen)
- enlarging causes pixellation
- support transparency so can be used on any background.
-
for the web
- can be stored in many formats
- easy to produce
- can be output from many apps
- created from 2 dimentional arrays of pixels
- can display many colors
- depending on bits per pixel
- can display gradients / grayscales
- photo realistic
- can edit to be more attractive
- can easily translate to dot format
- printers / CRTs
- can be used in simple animations
- eg: animated GIFs
- can compress to reduce loading times
File Formats��
-
files
- contains pixels and metadata
- pixel has color depth (number of colors)
- metadata is data about the file
- image source
- copyright information
- device information (which phot was taken from)
- file format may allow compression
- compression maybe lossless
- or lossy
-
why?
- some software may not support all file types
- so, have different export options
-
- some are compressed
- eg: JPEG (lossy)
- some are compressed
- most universally supported are:
- JPEG
- no transparency support
- no animation support
- supports more colors (high color depth) than GIF
- GIF
- supports transparency
- supports animations
- JPEG
- some other types
- TIFF
- highest quality
- gives largest file size
- BMP
- only supports windows OS
- TIFF
- some software may not support all file types
JPEG
- description
- both lossy and lossless compression
- used for web
- supported by web browsers
- suffers image degradation
- (when repeatedly edited and saved)
- need more processing power (to compress)
- no transparency support (easily)
- doesnt encode large uniform areas of colors well
PNG
- description
- lossless compression
- FOSS
- works in web
- performs well with large uniform colors
- works well when progressively downloaded
BMP
- description
- large file size
- used by microsoft tools
GIF
- description
- works in web
- supports animation
- allows several images in one file
- no color management (in different devices)
- so, colors may alter
- only limited number of colors
- 256 colors
TIFF
- description
- stores 24-bit colors by using 48-bits per color
- uses lossless compression
- LZW Algorithm - no data loss
- not supported by web
- large file size
- doesnt support interlacing
- doesnt support animations
Vector Images
-
advantages
- easier to edit
- Editing does not affect the quality
- does not pixelate on enlarging
- have smaller file size
- saves storage
- download faster than bitmap image
- so can be displayed on low-power devices
- Edges are smoother
- well defined (in SVG)
- producing a higher quality image
- supports transparency
-
disadvantages
- Photographs are not realistic
- surfaces are unrealistic
- Small editing errors are more visible
- reduces the image quality
- hard to add special effects is more difficult
- hard to add color graients
- need powerful devices
- to carry out calculations
- when editing
- may vary on software being used to view
- converted to raster/bitmap images before displayed on screen/monitor
- Click here to learn more
Structure
- node
- what
- Control point for paths in image
- Has defined positions on the x- and y- axes
- Determines direction/vector of path
- Defines/shows the start and end points of paths.
- node editing
- (related to 'Vectors Images - Editing' section)
- nodes can be joined together
- moved to change the path direction
- Add a new nodes (to change shape)
- Delete a node
- symmetrical nodes
- to create smooth flowing curves
- asymmetrical nodes
- to obtain a different amount of curve on each side
- of the node (keeping a smooth flow through the node)
- cusp nodes to create extreme changes in direction
- change the length and direction
- of each control arm independently
- smooth nodes
- for smooth transitions between straight line segments
- what
Tools / Techniques
- to change appearance of objects
- Use of Bezier handles to change angle of line / control-point
- Moving node to change the start/end points of
- Bezier curves (that make up rounded shape)
- Moving node from one position to another
- Adding node to line to divide line into two and moving new node
- Deleting nodes to join lines and remove curves
- Group shapes to allow for movement of parts of images
- Changing the colour/transparency/size/rotation of shape
- Manually editing the code in the SVG XML file.
File Formats
-
svg (scalable vector graphics)
- why
- open-source
- a W3C standard (World Wide Web Consortium)
- based on XML which is standardized
- can be imported into many graphics software
- Format is scripting, so can be used with CCS
- supported by web & print systems
- No compression applied
- Use of XML + mathematical calculations
- image can be scaled without quality loss
- information stored
- The font to be used.
- shapes
- dimensions
- position on screen
- style
- colors to fill shape
- lines
- dimensions
- position on screen
- colors to draw line
- why
-
how it resizes without quality loss?
- vector images are mathematical expressions of shapes/paths (to create images)
- Shapes include lines/polygons
- Points defined with x-y axes and direction of path
- Shapes and positions are recalculated every time the image is resized
- so quality is retained
- Lines in vector images do NOT change proportionately when resized
- bitmaps
- consist of a set number of pixels
- when resized
- number of pixels change
- lines change proportionately
- so, quality is altered
Uses
- outline fonts to describe printable characters
- as svg on web pages (HTML5)
- used by pen plotters to draw shapes on paper
Common
Stuff
- resolutions
- basics
- Resolution is measured in PPI (pixels per inch)
- Low resolution images
- few pixels
- High resolution mages
- many pixels
- have higher quality
- looks crisper
- why different resoltions needed
- for (professional) printing
- need high resolution
- 600ppi or more
- images for magazines
- 300ppi
- Poster images on bill boards
- 150ppi
- low, cuz viewed from far distance
- viewing on screen
- matches PPI of screen/monitor
- for web
- mid: 72ppi or 100ppi (modern retina screens)
- for fast loading
- but enough quality to view
- use pixel dimensions
- (not resolution)
- can have differing resolutions
- but display at same size
- (and looks the same)
- for presentations
- standard: 1024x768 + 72ppi
- (projectors, large TVs)
- for (professional) printing
- basics
Colors
Color Systems
-
RGB
- stuff
- use additive colors (to create color ranges)
- adding all colors together -> white
- used in computer screens
- stuff
-
CMYK
- stuff
- use subtractive colors (to create color ranges)
- adding all colors together -> black
- used for printing
- black has to be added
- CMY is muddy brown color
- so, most printers use black catridge when printing CMYK
- (inkjet printers, both catridges being used)
- black has to be added
- stuff
-
HSL (in Web Development Chapter)
- not sure if it also belongs here...
-
comparisons
- RGB vs CMYK
- similarities
- color codes for defining colors
- can produce many colors
- from white -> black
- highly supported by many apps
- affected by differences in display media
- similarities
- RGB vs CMYK
Editing
Components
- layer
- level at which an object is placed in an image
- represents part of graphic (as pixels in bitmaps)
Editing Tools
-
layer tool
- what it does
- To separate elements of image
- to worked on independently
- To overlay elements onto others
- each element can be moved independently of the others
- allows editing of elements while leaving other elements untouched
- do stuff to one element/layer (without affecting others)
- allows transparency effects (of objects)
- To insert text
- writing can be placed anywhere on the image
- To separate elements of image
- how to use it
- adjust transparency to allow other layers to be seen
- can overlap to create composite image
- can replicate to show copies (of same thing)
- can replicate to mask parts of image
- to ajdust brightness / saturation
- what it does
-
flatten tool
- To merge all layers into one layer
- To discard hidden layers
- make all layers are visible
- To fill any transparent areas with white 'background colour'
- to create pdf to print easily
- To reduce the file size
-
color gradients
- types
- linear
- fills evenly across image
- radial
- (center -> outwards (along radii))
- fills with single line path
- fill starts at centre
- to outwards along all radii
- fills evenly along all radii
- elliptical
- fills with two line paths
- fill starts at center
- fills outwards
- along two directions away from the center
- can be skewed along one line or another
- conical illusion that image is cone shaped
- square fills
- produce a start like view in color
- three color fills
- merge from one color into two (across the image)
- four color fills
- merge from one color into three (across the image)
- X color fills
- merge from one color into
X-1colors (across the image)
- merge from one color into
- linear
- what to change of a filled shape?
- opacity
- from opaque to transparent
- fade color from one color into another
- opacity
- types
Conversions
-
bitmap to vector
- how
- (Clearly defined) areas in the bitmap are automatically traced to create objects in the vector image
- Nodes are added to the objects
- Object manually corrected by user to merge shapes
- Colour resolution (number of bits) reduced by user
- how
-
converted to raster/bitmap images before displayed on screen/monitor
- why?
- Vector images are stored as co-ordinates
- geometric descriptions of shapes and colours
- Digital monitors cannot display co-ordinate-based graphics
- Because all digital monitors are pixel-based
- Graphics card converts the co-ordinates into pixels before sending to digital monitor
- Uses an ADC-type action
- Resizes the image to suit the monitor.
- Vector images are stored as co-ordinates
- why?
Comparisons
- bitmap vs vector (for web)
- photo realism
- Bitmaps are comprised of small pixels so the bitmap is the most suitable format for photo- realistic images or images with high amounts of fine detail.
- The vector image, on the other hand, does not possess the same kinds of photo-realistic capabilities because it is comprised of larger objects and cannot achieve the kind of fine detail that is necessary for photo-realism.
- scalability
- Vector images are made of mathematically defined objects so sizes can be easily manipulated with little to no loss in the quality of the image.
- The objects within a vector image are re- rendered at a greater or smaller scale to provide consistently smooth edges.
- Bitmaps are more difficult to scale because changing the size of a bitmap requires a complete rearrangement of the pixels.
- An enlarged bitmap is likely to appear blurry, or "pixelated," meaning that the different pixels of the image have become visible.
- shape
- A bitmap image always has four straight edges while vector images can be any shape
- file size
- Complex vector images can have a very large file size due to the complex instructions needed to create them;
- the size of the file is not dependant on the size of the image:
- small complex images can have a large file size;
- bitmap images can be large but can be compressed.
- conversions between file types
- The most common file type for bitmap web images are jpeg or gif, and conversion to these is simple without loss of quality;
- conversion of vector images often results in more loss of quality.
- photo realism