6. Software Development
All Past Paper Questions: https://docs.google.com/document/d/1yzrwajG6hW2RexRY177O6ISq-HIMi12RvZjx3vnOa5c/edit?usp=sharing
Questions left out:
- p3-ch3-pg80
- p3-ch6-pg69
- p3-ch6-pg71
- p3-ch6-pg75
SDLC
- stages
- list
- analysis
- design
- development
- testing
- implementation
- documentation
- evaluvation
- maintainance
- how they are related
- each stage has to be completed
- before starting the next stage
- deliverables
- from this stage is used in next stage
- of one stage scan be used to revisit previous stage for alteration
- process can be iterative with repeated movement
- between adjescent stages
- documentation from each stage
- used to produce System documentation
- outcomes compared with initial requirements
- maintainance stage can result in revisiting the design stage to restart cycle
- each stage has to be completed
- list
RAD
- stages (summarized)
- determine user reqiurements
- create early prototypes (function, quickly)
- gather feedback
- use it to create high quality feedback
- reapeat his until software is finished
- test prototypes throughout development
- crease user documentation
- produce final product for rollout to users
- stages
- requirements phase
- define project in terms of what needs to be developed
- gather user requirements
- define data flow
- plan processes for managing project
- eg: risk assestment
- planning tasks/activities
- data modelling / requirements phase
- analyze requirements
- create sets of data objects
- define relationships between data objects
- define test plans
- define training strategies where required
- determine implementation method
- process modelling / user design phase
- define process for any changes
- define process for adding a data object
- users interact with System analysts to develop early prototypes
- application creation / construction phase
- making prototypes by experts
- coding can be automated
- can code many components simultaneously
- user evaluvation of prototype
- repeated testing by users
- and suggests improvements
- implementation / cut over phase
- carrying out test plan by testing data flow
- testing interfaces between components
- testing the complete System
- user training
- rollout of 'app' to users
- requirements phase
- why (instead of waterfall)
- project divided to small subtasks
- (teams can work concurrently)
- subtasks can make use of specialised teams
- prototypes created quickly
- development time is not wasted,
- prototype does not work as intended
- (waterfall method) if project fails, start again
- can adapt changes in user requirement
- can work well when developers telework
- changes made before final product is created
- client not surprised by unexpected end product
- project divided to small subtasks
- advantages
- Increased quality
- focusses on problems to end users
- rather than technical problems (of interest to developers)
- complete project on time
- within budget
- uses incremental development
- low chance of failiures
- More risk control
- the key risk factors show in the early part of the process
- so, adaptable process
- Increased quality
- disadvantages
- Users involved from beginning & at all stages
- takes more interaction between users and devs
- time consuming for developers
- higher costs
- RAD can be new for some developers
- new tools more likely to fail
- adaptable
- Less control over the process
- bad design of prototypes
- constant (minor) changes to components
- ignore system architecture issues
- Not suitable for very large systems
- Users involved from beginning & at all stages
Agile
- agile software development
- for
- customer satisfaction is highest priority
- (from early to late stages of development)
- can easily manage changes in requirement
- produces working software for client in short period of time
- devs must work together
- face-to-face conversation (more efficient)
- promotes constant pace of development
- iterative testing, so
- errors corrected quickly (constant testing)
- teams are allowed to self-organize
- leading in better wokring practices
- customer satisfaction is highest priority
- against
- face-to-face daily meetings means must be in same workplace
- travel costs
- cost estimates change over time
- milstones difficult to set
- uncertain about what they will address in the near future
- face-to-face daily meetings means must be in same workplace
- describe / stages
- initiation
- Create idea for project
- Discuss ROI (return on investment)
- Identify team members
- Determine required time/resources
- Carry out feasibility study
- (determine if the project can be done)
- planning
- Developers working with end-users
- Specifications are written
- User/system/requirement specifications
- Risks are considered
- Product features are determined
- development
- Development based on specifications
- Occurs in iterations (incremental phases)
- Working software
- available at end of this phase
- with minimal functionality
- Each iteration is tested
- documentation
- Production of user documentation
- Deployment to end-users
- Handover with training to end-users
- Software monitored for errors
- support/maintainance
- Software (end-of-life) decommissioned
- Support for software stops
- End-users notified of impending withdrawal of software
- Software replaced by new (version) release.
- initiation
- for
Waterfall Model
-
stages list
- analysis/requirements
- design
- development/implementation
- testing
- documentation
- evaluation
- maintainance
-
introduction
- linear approach
- client requirements gathered at start
- uses Gannt charts to manage development changes
-
phases / stages (new, short)
- create requirements
- analyse to create models / schemes
- design to create technical designs
- implementing the code
- integrating units of code
- create techinical/user documentation
- testing (using a test plan)
- deploy software by
- installation
- migration
- support
- maintainance
-
phases / stages (old, long)
- linear apprach
- traditional
- produce requirements document
- analyze it
- produce model
- design the softwre
- produce DFD / system flowchart
- unit test the source codd
- integrate these units into whole system
- do whole system testing
- revisit code improvements
- carry UAT (user acceptance testing)
- remedy any issue discovered
- develop support mechanism for users
- deliver the finished product
-
advantages
- issues found in early stages (and fixed)
- emphases on full documentation
- eg:
- requirements documents
- design documents
- so, can replace anyone in the team easily
- eg:
- development is structured
- (through seperate stages)
- stage easy to understand
- allows milestones to be set
- ensures all requirement are met
-
disadvantages
- requirement not fully known
- clients may change their requirement
- may not cover all details
- clients may not know exactly what they want
- expensve, since has to change a lot
- deisgners unaware of future difficulties
- clients cannot see functional prototype during development
- difficult to change at middle (during development)
- since requirements are already set
- requirement not fully known
Analysis
-
data collection
- stuff in P1-CH1 and P3-CH1
- document analysis
- advantages
- less time consuming than other methods/more efficient as it
- requires data selection rather than data collection
- many documents are readily available/in public domain
- documents unaffected by research process
- documents are stable/do not change due to observer's presence
- documents can be more exact/precise
- documents provide wide/broad coverage of topics
- disadvantages
- documents may lack detail as not produced for research
- documents may be difficult to retrievenocate
- documents may be incomplete
- questionnaries
- advantages
- relatively inexpensive to administer when large numbers are involved
- reduced researcher bias
- questionnaires are familiar to participants
- data can be collected in a format that is easy to analyse
- disadvantages
- participants may not complete questionnaires/return the
- questionnaires fully/properly leading to incomplete data
- questions may not mean the same to all participants
- may be unclear who has completed the questionnaires
- unable to develop the questioning further
- questionnaires can be difficult to formulate
- advantages
- observation
- can collect data where/when activity occurs
- can be unobtrusive
- can provide 'behind the scenes' information/can directly see the activities
- can be susceptible to observer bias
- observed often perform better when watched
- cannot help understand why people behave as they do/do what they do
- advantages
- data collection from staff
- managers
- interview face-to-face, before asking opinion
- managers can be available for additional questions
- not many managers, so, less time
- interview face-to-face, before asking opinion
- assembly-line workers
- observation
- to not distract them from work
- observers can see process for themselves
- dont need to know technical language
- observation
- clerical staff (data entry, customer service, etc...)
- questionnaires
- can take them home and do it in a free time
- can be anonymously returned
- observation (bad)
- behaviour changes quickly
- interview (bad)
- too much staff
- clerical staff can remain anonymous
- questionnaires
- managers
-
data input
- online forms
- explain
- done by clerk
- provides feedbkac + shows progress
- ensures instructions understoof by clerk
- ensures language is consistent
- can prevent errors
- validation techniques
- can correct mistakes
- suggest correction
- shortcuts to maximise performance
- reduce unnessesary information
- to not confuse the clerk
- provides documentation when additional explanation is required
- explain
- forms (/ details collected)
- form checks
- check
- data entered to field
- data within pre-set ranges
- eg: dates of bookings
- data in required format
- eg: email address
- data against pre-set values (lookup tables)
- eg: title of employee
- data entered is of required type
- check
- form controls
- data is lost in form and submitted to back end on form submit
- buttons
- clicked to activate a task
- submit button
- send form data to backend
- reset button
- clear form
- custom can re-enter data again
- hidden buttons
- not rendered by web browsers
- check boxes
- (sharing the same name)
- allow multiple choices
- eg: choices of food
- when check, attribute set the switch is 'on'
- only 'on' states submitted with form
- radio buttons
- mutually exclusive switches
- (sharing the same name)
- only one choice can be made
- eg: male or female
- text input
- single line input
<input>- eg: for name
- multi line input
<textarea>- eg: additional requirements
- single line input
- (dropdown) menu
<select>,<optgroup>,<option>- provide pre-list of options
- eg: destination, departure
- file select
- to select files to submit on form
- characteristics of a well designed form
- show only required info
- simple sentence structure
- no technical jargon
- consistent format to find information
- labels should
- be right-justified to left of input field
- use a colon, capitalize maybe
- compatibility with other input screens
- information should be in logical order
- should not be repeated
- form checks
- online forms
-
examining documents
- preparing
- identify documents to explore
- consider how they will be accessed
- language & cultural barriers
- acknowledge and address biases in humans
- consider relevance of document
- be clear about what to searching
- consider ethical documents
- eg: confidential documents
- consider alternative sources (if requested)
- examining
- gather relevant documents
- develop organization and management
- produce data flow diagram
- determine src/dst of documents
- make copies of originals for annotations
- assess authenticity
- examine
- purposes
- background information
- the content
- keep records of observations
- preparing
Design
-
design specification (document)
- why
- specify criteria for development
- give guidance for developers
- specify how System will meet user requirement
- form part of patent application (for the desing)
- form basis of accurate costing
- be a part of legal contract between client and developers
- contents (for a DBMS)
- document stating
- purpose for design
- description (for intended audience)
- for purpose of calculations
- of formulas and calculations
- error handling requirements
- backup/recovery procedures
- System startup/shutdown procedures
- validation performed
- and error messages shown
- layout of report
- securitu design
- access control mechanisms
- audit log provision
- user authentication
- encryption process
- identify intended products
- using names and references
- summary (of contents)
- overview of design
- relationship between data elements
- file requirement description
- eg: file access methods
- document stating
- why
-
good designs
- on screen input (form)
- should be straight forward
- to reduce misunderstanding
- consistent
- simple to use & obvious
- clear design with enough space
- keep necessary keystrokes to a minimum to reduce time
- form should include validation routines
- use input controls
- provide immediate feedback
- appropriate use of white space
- should be straight forward
- on screen input (form)
Development
- developing source code and stuff, more info at RAD, Agile and Waterfall model
Testing
- strategies
- alpha testing
- leads to beta testing
- stuff
- usues white box & black box testing
- by employees
- uses lab/testing environment
- takes place under control of developers
- does reliability testing
- does security testing
- crtical issues fixed immediately
- gets a more technical analysis report
- features
- type of acceptance testing
- to identify erros before releasing to end users
- uses both black & white box testing
- usually work for the software developer
- describe (basically the same thing)
- done by the developers on the development site
- Carry out review of the
- requirements specification
- and design specification
- Create full test plans
- Create test data
- Carry out the test plans
- Record errors discovered during testing
- Determine the cause of errors
- Correct errors
- iterative testing until errors are fixed
- Uses both white and black box testing
- beta testing
- stuff
- involves black box testing (usually)
- by third-parties
- takes place under control of users
- features
- done by real end users
- in real environment
- final testing phase before release of product
- stuff
- other
- comparisons
- alpha vs beta
- similarities
- last tests before release
- done by other (other than programmers)
- impacts final quality of product
- similarities
- alpha vs beta
- for open source Operating System
- ensure writer of test plan knows what he's doing
- he should be able to
- define aspects of OS to be tested
- define test methods
- use smartphone facilities
- assing tasks to ensure smartphone functionality
- functionality of apps
- specific / custom written apps
- third party apps
- ability to multi-task
- test if sufficient memmory
- comparisons
- alpha testing
- test case
-
white box testing
- how
- developers / testers ...
- create a test plan
- create test data
- test every line of code
- test every branch in the code
- test every condition in the code4
- test calculations
- test the logic of code
- test inputs
- can use (automated) testing tools to check code
- errors are noted and corrected
- repeat the testing
- (must) have good knowledge of coding
- (must) understand how the code works
- advantages
- introspection - tester looks inside system
- identify system objects in code
- reduce the failure rate
- more stable
- allow re-use test code
- More complete testing of code
- all aspects of code
- every interaction in code
- all routes through code
- introspection - tester looks inside system
- disadvantages
- closely integrated with the system
- installed in the system
- not sure if testing is not causing the errors
- not all platforms support this
- changes to objects cause it to fail
- highly integrated with system code
- more maintenance
- Tester must have in-depth knowledge of system
- skilled programmer
- closely integrated with the system
- how
-
black box testing
- advantages
- easy to use tested
- dont need to know how it works
- dont need programming knowledge
- can walk through app, as a normal user
- quicker development of test case
- tester only needs to look at GUI
- dont need to discover internal routes
- tests dont from POV of user
- can expose discrepencies in specification
- tests can be done by independent personell
- avoids developer bias
- test cases can be designed as soon as specification is complete
- easy to use tested
- disadvantages
- hard to design test cases
- as no clear test specification
- difficult script maintainance
- user interface changing due to testing
- scripts maybe fragile when working
- not the same GUI (for different tests)
- rendering may change
- doesnt test all internal pathways
- doesnt fully test software
- many program paths left untested
- hard to design test cases
- advantages
-
- tester reporting error (report)
- should have
- purpose of test
- how it was carried out
- special test environment that was created for the test
- expected reults
- actual results
- whether or not the software passes
- recommendations for testing the software
- should have
- test data
- why
- to find errors in logic / formulae
- to show errors in logic formulae
- confirm validation routines work as expected
- confirm given input
- gives expected output
- check error handling
- eg: abnormal inputs
- why
- test plan
- importance (new)
- ensure requirements are met
- acts as instructors for screen
- allows management of any changes
- needed during development
- defines test to carry out
- records results of test for later analysis
- importance (old)
- overview of all testing
- Systematic outline of all features
- continuously checked
- prepare that all aspects of running a test are considered
- train those who need to assist with the test
- mechanism for outlining test needs
- lists limitations
- lists reasons for testing
- Ensures legal issues are met
- to show regulatory bodies
- that testing has been carried out
- overview of all testing
- importance (new)
Implementation
-
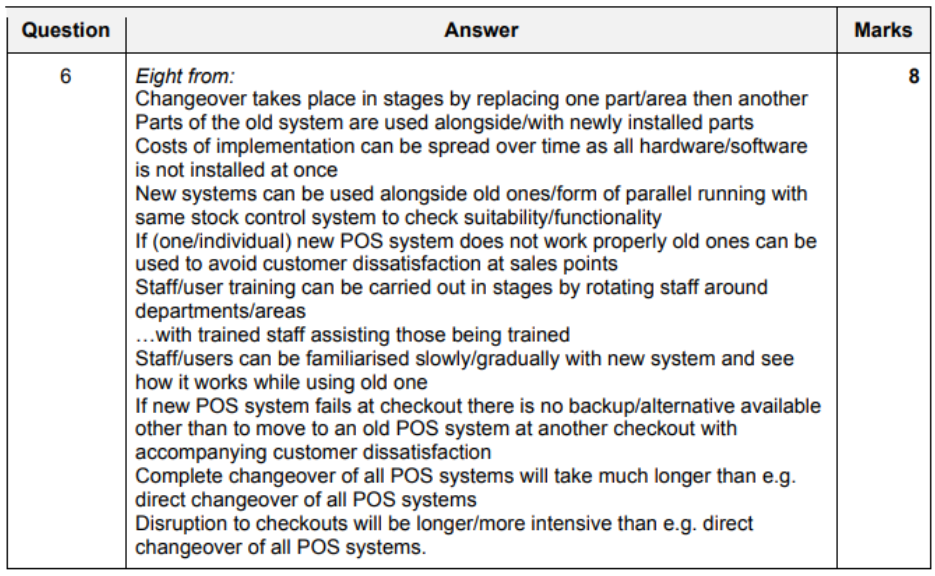
pilot running
- advantages
- if System fails
- only one part fails
- easy to manage implentation at once
- than a full direct change over
- staff can be trained in small groups
- staff can learn from mistakes (made by grouping)
- trained staff can support training staff
- only part of company is changed
- implentation costs can be phased over a longer time period
- saving company money (large costs at once)
- if System fails
- disadvantages
- full implementation takes time
- eg: direct change over
- can cause more disruption (to company)
- IT staff has to support two teams at the same time
- (unlike direct changeover)
- old and new Systems have to interact data
- so, data is at risk of loss
- data lost if System fails
- full implementation takes time
- advantages
-
phased implentation
- question
- effectiveness
- done part by part
- implementation done in stages
- time is available for adjustments
- users have time to adjust
- technical staff concentrates on one part
- problems (that arise) at start are less critical
- training confusin for users
- used to old System
- less productive
- System delivery unclear
- long duration of change over
- users workflow disrupted
- more disruption to bussiness
- check integrity of data before adding new module
- 'fall back' to each stage becomes more difficult
- implementation unclear
- increases complexity
- lack of motivation
- need several adjustments
- at later stages
- fall back to old System
- becomes impossible
- so, should use half-completed new System
- question
-
parallel running (during migration)
- advantages
- can compare results (to ensure there's no error)
- can use existing System
- while deploying new System
- so, production is not stopped
- can use existing System to rectify errors
- staff can be trained on new System
- so, staff is confident
- disadvantages
- expensive
- need to pay for two sets of hardware
- production slows down
- staff needs to update both Systems at once
- need to input data twice
- increases data entry
- to ensure accurate input to both Systems
- high maintainance time
- slow production
- more expensive
- expensive
- advantages
-
change over implementation
- prepare
- ensure management
- to determine what needs to be done
- after change over
- train staff supports training staff
- train technicians to maintain new System
- prepare user manuals
- ensure data is secure
- confirm compatibility
- ensure hardware availability before installation
- transfer/migrate data from old to new System
- test new System
- ensure management
- advantages
- can change System in convenient time
- eg: after a shop is closed
- benefits of new System are available immediately
- can be carried out quickly
- with minimal disruptions
- can change System in convenient time
- disadvantages
- if new System fails, old System is not available now
- may loose data as old cannot be installed
- staff has less time to learn System
- so, maybe more errors
- prepare
-
examples
- bank replacing their Systems. ensure it carries all the functions. without interruptions.
- start both Systems at the same time
- copy everything to the new System
- new customers register to new System
- switch all services (after System is installed and running)
- compare speeds/results
- long time period to test
- still keep the old System running
- ensure everything is duplicated in full
- no difference to staff or customers
- after new System tested successfull
- complete the switch
- run the old System as a backup (for a short period of time, incase of a sudden failiure)
- example 2
- large company. replace current systems. large workforce with many departments. time is not important (no hurry). should be as efficient as possible.
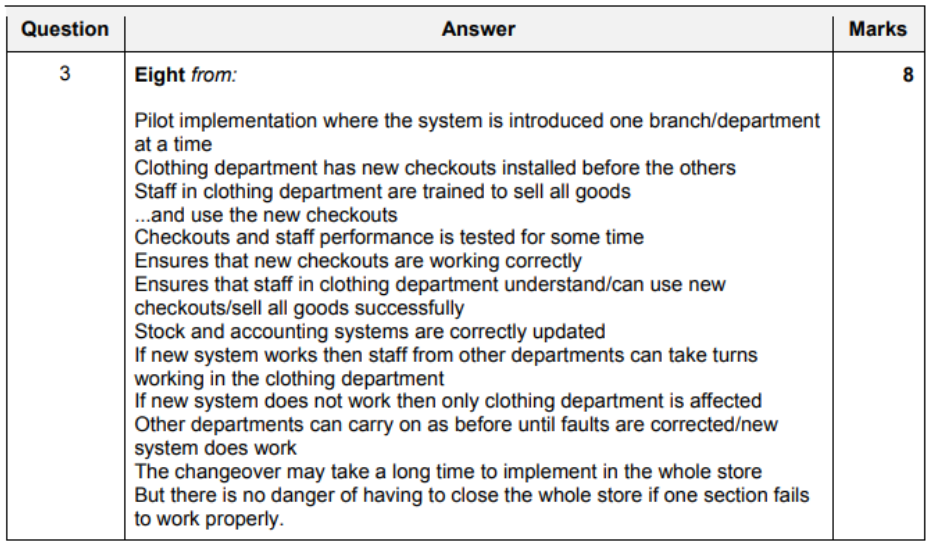
- Pilot running
- not appropriate
- each department would not need similar aspects of the system
- Phased implementation
- would be possible because one department could have their part system implemented
- when working another part of system could be tried in another department
- Parallel running
- enough workers available to use both systems at the same time
- Parallel running
- company can afford to employ two sets of workers if more are needed
- old system continues while problems are fixed with the new system
- Direct changeover
- bad, as it may not work property first time
- quick method but speed of changeover is not an issue
- cheaper method but the cost is not important to the company.
- Pilot running
- bank replacing their Systems. ensure it carries all the functions. without interruptions.
Documentation
- types
- technical documentation
- purpose
- for use
- after delivery of software
- by technicians
- when maintaining the software
- when re-developing the app
- allows completion of program
- (when the original programmer is no longer available)
- for use
- why
- so installer knows what hardware is required
- data structures can be amended by analyst
- programmer understands how data flows
- to provide basis for technical writers
- provide reference for programmers
- why (new programmer working on project)
- Program listing (can see full details of code)
- List of variables (to follow the parameters)
- Program flowchart (overview of program)
- Notes (know where to start)
- Test plans + results (can check code)
- Known bugs (to correct)
- Purpose of software + reasons for choosing library (instead of custom code)
- Input and output data formats (write code to match)
- information to include
- comments explaining how code works
- comments on use of variables
- data structures used
- file naming conventions used
- detailed of used validation routines
- navigation layout
- database details
- tables & their purpose
- relationships
- explaining stages of macro script
- records of test logs and test results
- security method details
- details on how software can be installed
- details on how to backup + restore app
- purpose
- user documentation
- describe
- explains end-users the functions of software
- and how to carry out tasks
- describe
- requirements specification
- describe
- details user requirements
- describe
- System specification
- describe
- details software and hardware needed
- describe
- design specification
- describe
- details of what software will be able to do
- describe
- technical documentation
Evaluvation
- how
- determine if now System is better (time saving)
- if easy to use
- (+ requires less training)
- go through requirements one by one
- compare with requirements specification to check that all requirements have been met
- get user suggestions
- identify issues/problems
- SDLC to started again to correct the issues
- ease of use
- could be examined
- (to check if its easy to do stuff)
- installation procedures
- start-up procedures
- end-users can access and use as required
- user navigation
- System producing required results
- with less errors
- are features easy to find
- assesment of user acceptance (of new System)
- well structured user documentation
- trouble-shooting advice to help users
- purpose
- to check whether or not the new System
- meets specifications set by analyst/designer
- meets the designs
- has expected behaviour
- has problems
- and how they might affect the funcationality
- determine opportunies for adding new feature
- to check whether or not the new System
- could be examined
Maintainance
- meaning
- correcting a problem in the System
- after System is broken
- restoring functionality
- steps
- diagnose the problem
- (by testing System modules and components)
- gather information (logs and users)
- identify the problem
- isolate faulty code/component
- replace it with a new component
- test it
- check and remove viruses
- re-format storage devices
- perform a System restore
- refer to technical documentation
- make a report for reference
- re-test System at the end
- diagnose the problem
- why
- ensure the System works
- for its expected life time (until bussiness requires it)
- types
- corrective maintainance
- why
- correct errors in program code
- so, System works properly
- why
- perfective maintaince
- why
- improve functionality in System
- remove unwanted functions
- to make it more suites to needs
- why
- adaptive maintainance
- why
- System remains compatible
- with changes to maintainance
- why
- preventive maintainance
- why
- prevent problems caused by
- eg: security vulnerabilities
- prevent problems caused by
- why
- corrective maintainance
- maintaining an error free system
- error-free, corrective maintenance is not needed
- no new situations to arise, adaptive maintenance is not needed
- Perfective maintenance is needed
- to modify the code
- enhance capabilities
- to increase usefulness
- Delete unused functions to reduce the complexity & resource usage
- Optimise code
Corrective
- description
- modifies software to correct problems
- that have been identified in error reports from users
Adaptive
- description
- updates software after delivery to the users
- In response to
- new environment
- changes in industry
- business requirements
- changes to regulations & legislation.
Preventative
- description
- updates software after delivery to the users
- To avoid possible errors
- that might occur in the future
- To fix errors that do not affect function
- (eg: CSS issues)
- (but may become significant in the future)
Perfective
- description
- Enhances
- performance after delivery
- (during the lifetime of the software)
- user experience
- reliability + security
- (to increase its life span)
- the ease of maintenance of software
- performance after delivery
- Enhances
Unknown / Uncategorized
-
new UI for doctors to access patient records
- meaning
- implementating the change in one center
- before implementing the change in remaining centres
- for
- issues in one facility can be fixed
- (before addressing the other)
- reducing the overall problems
- users have access to new System + docs
- they can assist others in its use
- workload can be spread out over time
- technicians required to fully implement new System
- disruption caused in less
- so, less danger to patients
- user feedbacks to assist training
- improving user experience at centers
- less impact to patient care
- issues in one facility can be fixed
- against
- more time taken
- to be available at all centers
- more expensive
- ?? IT staff will have to be relocated multiple times ??
- other staff moving between centers
- should be familiar with both new and old UI
- motivation of staff may decrease over time
- slow work
- more time taken
- meaning
-
feedback
- focus groups
- interview with smaller people
- members often have similiar ideas
- stake holders can suggest ideas
- moderator discusses a conclusion
- gives accurate information in a short time
- cheap
- but expensive if carried from wide range of people
- results affected by (presence of) interested parties
- validity of outcomes maybe questionable (in front of stake holders)
- outcomes not confidential
- participants often from external sources
- focus groups
-
prototyping
- advnatages
- customers need changes
- so, high costs
- quality can be improved by testing prototypes
- prevents disasters at end
- discovered in early prototypes
- saves money
- need more client involvement
- show working model first
- means clients are more aware
- customers provides immediate feedback
- meeting expected results
- reduces miscommunications
- end product more closely meets requirements
- avoids later changes (saving time)
- customers need changes
- disadvnatages
- insufficient analysis (deviated focus)
- may overlook problems
- overlooking better solutions, so, poor specification
- so, bad engineering
- hard to maintain
- users might confuse prototype with actual product
- (might assume the final product is incomplete)
- user might need all features in prototype
- slowed development
- prototypes take time to develop (so, more expensive)
- insufficient analysis (deviated focus)
- use
- issues detected during development
- users involved at all stages of development
- users can interact with app
- and give feedback
- incooperated during development
- users get a better understand of the product
- to investigate potential market for the app
- types
- incremental
- characteristics
- project broken to sub projects
- product partially built on previous iterations
- requirements produced first and completed
- testing at each iteration
- requirement -> development -> testing -> stop
- advantages
- whole System clearly defined and understood
- early user feedback
- minor details allowed with time
- allows additional features to be added
- builds on a basic foundation
- divides final product into parts
- parts developed seperately
- easy to identify errors
- testing and debugging can be done
- product must sell early
- new technology being used
- required skills not available yet
- disadvantages
- affects functionality of earlier versions
- may be not all requirements produced
- high overall costs
- characteristics
- throw away
- stuff
- discarded at any stage
- produced quickly and cheaply
- maybe non functional
- more user involvement
- easy to measure progress
- easy to set time-scale
- reason to use
- to ensure System requirements are valid
- and understoof by all
- quickest method to obtain feedback
- to ensure System requirements are valid
- advantages
- speed with which the prototype is put together
- ensure the requirements are clear (ly understood)
- focuses the user on only one aspect of the system
- keeps the feedback precise
- disadvantages
- developers might be pressured to developing unfinished products
- user might confuse it with final product
- prototype may not work well
- lot of time wasted
- developers might be pressured to developing unfinished products
- stuff
- evolutionary
- stuff
- becomes a part of the final product
- developed over time
- functional from the inception (from start)
- stuff (compared to throw-off)
- client may decide that the early version is all that is needed
- Developers can focus on developing parts of System
- Instead of developing a whole System which might be beyond their comprehension
- Improvements to the System can be created later
- First prototype is not discarded so time is not wasted
- Throw-away prototypes may not work at all
- Can be used in interim until final System is complete.
- advantages
- delivery of the system is speeded up
- user engages with the system
- system more likely to meet user requirements
- disadvantages
- extended development time
- comments come from a biased/small group
- stuff
- comparisons
- throw away vs evolutionary
- similarities
- develop early prototypes
- no full requirement
- devs and users interact frequently
- end users can add/request features
- use interactive reviews
- similarities
- throw away vs evolutionary
- incremental
- advnatages