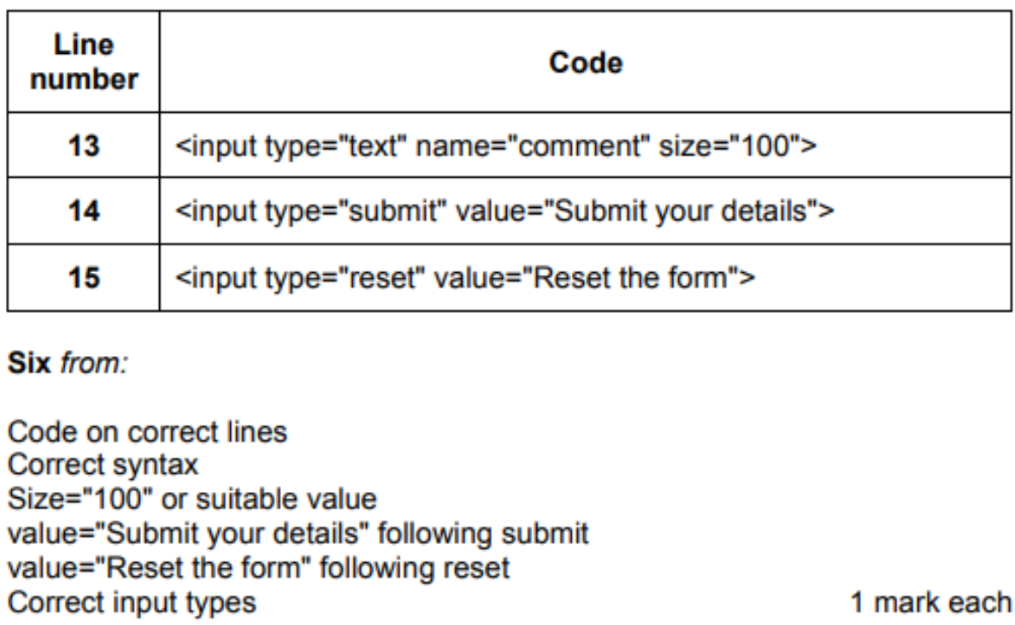
11. Web Development
All Past Paper Questions: https://docs.google.com/document/d/1huzD3ywePF8riWc9sYnAZJBI1650B5WlNi45cHm9f9o/edit?usp=sharing
Terms
General
-
operand
- numbers used in arithmetic operations
-
operator precedence
- order of performing arithmetic operations
-
assignment operator
- to give a value to a variable
-
literals
- fixed values (/numbers/strings) assigned to a variable
-
string
- text/characters within double/single quotes
- to store and manipulate characters
-
global
- variable declared outside function
- used throughout script
- value assigned to an undeclared variable
-
regular expression
- sequence of characters to search from
- character patterns used with functions to search strings
- a description of whats being searched for
-
operator
- arithmatic operators
- to perform (arithmatic) calculations
- or logical operators
- to compare values
- arithmatic operators
-
statement
- instructions to be executed by interpreter
-
array
- stores multiple values in a single variable
- why?
- suitable for storing a large number of items
- reduced complexity of code
- easy to understand
- increases code execution speed
- can loop through
- using an iterative function
-
variable
- containers for storing data values
-
function
- block of code to do a task
- executed when 'call'ed
-
comment
- types
- single line comment
- like:
// comment here
- like:
- multi line comment
- like:
/* body of the comment */
- like:
- single line comment
- description
- used to explain code
- ignored by interpreter
- ?? used to halt execution of code ??
- why
- to explain what code does
- to make code more readable
- doesn't affect intepreter, its all neglected
- accessing elements
- example
var cities = ["London", "Cambridge", "Oxford", "Manchester"]- access single elemtn
var place = cities[2] - access first 3 elements
for (i=0, i<=3, i++) { // 0, 1, 2 -> then break
document.write( cities[i] )
}
- access single elemtn
- example
- types
-
object
- collection of variables and functions
- represents attributes & behaviour of an 'item'
-
expression
- any valid unit of code resolves to a value
- types:
- can have a value
- can assign a value to a variable
-
terms (javascript)
- how object given a new property
- new property added
- by declaring a value
- display properties using loop
- JS code enclosed in HTML for use
- use of
for...inloop (JS) - define a variable (var/const) for storing (iterated) process
- specify objects to be examined
- enclose code within brackets -
{} - include code to count iterations of loop
- use code to pass results to HTML to display
- eg:
document.getElementById("id").innerHTML = xxx
- eg:
- use
console.log(...)for debugging
- how object given a new property
Keywords
- description
- cannot be used as vairbale named
- what
- names of HTML
- objects / properties
- event handlers
- window handler objects
- reserved terms (used in other programming languages)
- names of HTML
Usage
-
embedded
- example
<script>
document.getElementById("text").innerHTML = "123"
</script>
- example
-
in a seperate file
- example
- index.html
<script language="JavaScript" src="index.js"></script> - index.js
document.getElementById("text").innerHTML = "123"
- index.html
- why?
- separate html and JavaScript code so easier maintain.
- Can re-use the code (from different pages)
- No need to have several copies
- Code only has to be tested once
- JavaScript File is cached by web browser
- reduced network usage
- slow loading times
- low browser performance
- webpage dont work (as expected) until everything loads
- Can separate code into different functional areas
- provides modularity to code
- example
DOM
- HTML element
- Component of a HTML document
- contained between tags.
- starts with
<name of tag>and ends with</name of tag> - Node which can have attributes.
- Node can have 'child nodes'.
- Part of the Document Object Model (DOM) when document is parsed (by browser)
- how to change DOM
- select element, by ID or by query Selector
- use
.innerHTMLto change it's contents
Operators
Logical Operators
-
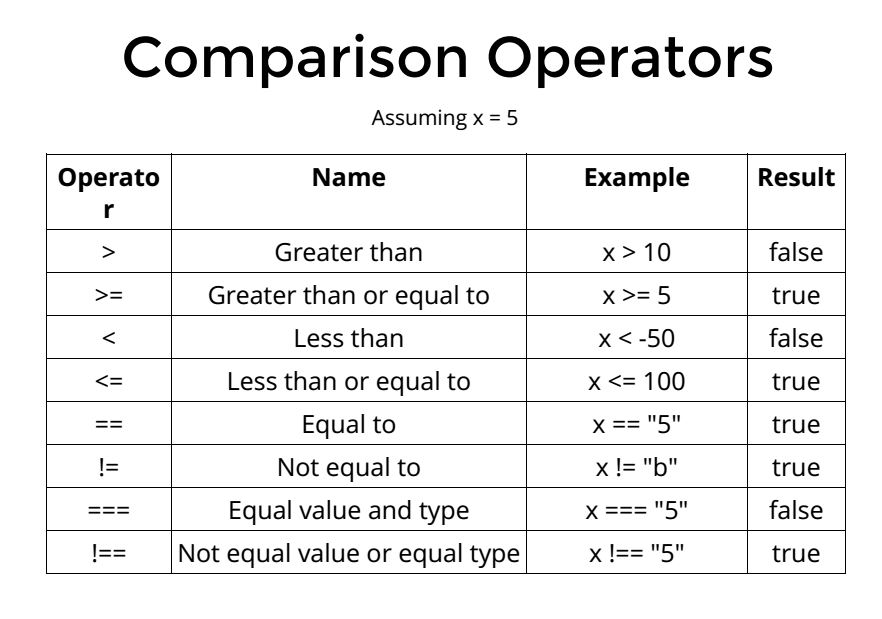
-
description
- Used in if-else/switch statements
- to test if conditions are true
- Compare the logic between variables
- Can be used
- with any data type
- in a more complex manner
- - complex conditions -
-
detailed explanations
==- converts characters to same type if necessary
- compares value to determine if strictly equal
- return
trueif same - return
falseif not same
===- compares both type and value
- return
trueif- same type AND same value
- return
falseif- same value
- different types
- return
falseif- same type
- different value
!==- compares both type and value
- return
trueif- same value
- different types
- return
trueif- same type
- different value
- return
falseif- same type AND same value
Iterations
-
what is an iteration method?
- repeatedly executes a block of code
- work through elements of array
- performs operation on every element of array
- works on element of array, one at a time
-
breakstatements- to break about a loop / switch-case
- the loop stops
- code outside is then executed
for loop
- how
- loops through a block of code, given number of times
- until condition is broken
- requires 3 expressions
- a declared variable
- expression to evaluvated
- at start maybe omitted
- at end, increment value ( of declared variable)
- incrementing variable at end is optional
- loop continues
- until condition is met
- forever
- if evaluvate statement omitted
breakmust be included- to exit the loop
- loops through a block of code, given number of times
- used when
- number of iterations known (beforehand)
- number of iterations
- pre-determined by iteration statement
- uses a counter
while loop
- test condition at beginning
- executes block if condition is true
- may never be executed
- tested before code block is run
- used when
- number of iterations is not known
- runs until
- condition is true
- until condition is met
do ... while loop
- test condition at end
- executes block even if condition is false
- always executed, atleast once (first time, before checking condition)
- tested after code block is run
Conditionals
if...else
- explain
- If ... else allows different actions to occur as a condition
- condition produces a Boolean result
- If TRUE an action is taken
- If FALSE another (different) action is taken
- Number is stored in variable
- Comparison operators to test valuewith variable
Tenary Operator
- Reduces code to a single statement to make code small
- take up less storage space
- Code is less complex to understand
- easier to wite
- less repetitive coding
- Code is easier to debug
- Can run multiple operations with code that is easier to follow
switch...case
- Variable declared to store a specified condition
switch(...)used to gather data to be tested against the variable- Use of case to create blocks of code that may be executed
- Variable with the condition listed for testing (against case)
- Use of break to end out of
switch(...)when variable matches case - Use of default at end of code block to specify code to be executed if no match found
Functions
- functions
- javascript objects with properties
- declared by function statement
- to save section of code for later use
- set of statements
- that performs a task
- and returns a value
- when valled
- only invoked when called
Inbuilt Functions
-
setTimeout()- stuff
- delays execution of code
- which runs only once
- minimum time is 0 miliseconds
- delays execution of code
- stuff
-
setInterval()- stuff
- allows repeated code execution
- at pre-set intervals
- minimum time is 10 miliseconds
- can stop the timeout timer
- so,
setTimeout()won't be executed
- so,
- stuff
-
confirm()- a dialog box with two elements appear
- OK button
- indicates acceptance
- Cancel button
- indicated rejection (of user choice)
- Message
- ask question
- or explains the choices available
- a Close button (in some browsers)
- to give no answer and close the question
- OK button
- why it may cause problems
- User's attention drawn away from main web page
- lose concentration (on page content)
- Input focus is taken away from the web site/pages until box is closed
- no other interaction is possible
- Other codes may stop functioning until the dialogue box is closed
- Position of dialog box cannot be controlled
- (may block information on page)
- some browsers may badly support it
- User's attention drawn away from main web page
- result returned back
- Return value
- is Boolean
- stored in a declared variable
- If user clicks OK then
trueis returned to variable - if cancel,
falseis returned - value in variable used to display stuff (with if-else)
- Return value
- a dialog box with two elements appear
-
prompt()- how to collect input
- variables declared to store values
- box pops up on screen
- can display default/sample entry in input box
- user must input value
- user presses OK
- if no value is entered,
NULLis returned - if cancel is pressed,
NULLis returned
- limitations
- position cannot be specified
- determines by browser
- may not be ideal for user
- appearance chosen by browser
- script is paused until box is closed
- additional code required to validate data
- some browsers support a default value feature
- position cannot be specified
- how to collect input
-
eval()- why not run string as code
- allows inserted code to run
- security issues
- why not run string as code
-
console.log()- writes message to browser console
- need supporting browsers (new versions)
- need to open console to see them
- used for testing purposes
- message within brackets will appear in console
- is a string / object
- is required
- can have more than one object
- objects can be variables
-
sort()- questions
- question 1

- answer
- treats values as strings not numbers
- Strings are sorted alphabetically
- Strings are not sorted numerically
- a is before than b so list 1 is sorted alphabetically by the first letter
- and then by the second etc.
- because 2 is 'bigger' than 1
- question 1
- questions
-
reverse()- reverses a string, a list, etc...
-
comparisons
setTimeout()vssetInterval()- similarities
- both are part of DOM (Document Object Model)
- (HTML Window Object)
- both takes two parameters
- first parameter: function to be executed
- second parameter: a time in miliseconds
- both can be interrupted using
clearInterval()function
- both are part of DOM (Document Object Model)
- similarities
Events
Event Handlers
-
onload- to run JS immediately
- after web page is fully loaded
-
onchange- execute code when state of value changes
-
onclick- when user clicks an HTML element
-
onmouseover- when mouse moves over an element
- (hover)
-
onmouseout- when mouse moves away from element
-
onkeydown- when a user presses a key / types
-
onerror- triggered when an exception occurs
- eg:
window.onerror = function_name(msg, url, line); - only captures error
- stores details for later
- function passes event details to alter box
- variables to pass paramaters of errors
- parameters
msg- message that browser displays
url- file name of code in which error occured
line- line which contains the error
Errors
Finding Errors
- questions
- question 1

- answer
- it does not work
- syntax error
- how the string
xis designed
- how the string
- strings must be enclosed in matching quotes
- quotes inside cannot be same as quotes outside
- either
'or"
- either
- or use a backslash
\to escape it
- question 1
Exception Handling
-
how
- use '
throw' to trap error - Use '
try' to handle the error - Use '
catch' to run code after if error- to show custom error message
- eg:
message.innerHTML = "Error"
- Use '
finally' to execute code regardless of error or not - Use '
error' to provide information about the error, eg:- EvalError
- RangeError
- ReferenceError
- SyntaxError
- TypeError
- URlError
- use '
-
how (2-old)
- add code to deal with errors
- without affecting web browser
- specify code block to be executed
try- block of code to be executed
catch- to define error handling
final- to allow code to be executed
throw- to display information about error
- specified message to display
- add code to deal with errors
Conventions
- declarations at start
- creates cleaner code
- single place to look for all local variables
- easier to avoid unwanted local variables
- reduce unwanted re-declarations
- initialize variables when first declared
- avoids undefined values
- create conside code, easier to follow
- single place to initialize variables
- always declare local variables
- local variables declared with
varkeyword - otherwise, they become global variables
- local variables declared with
Program Execution Flow
Questions
-
question 1

- answer
- Script embedded in HTML code
- between
<script> </script>tags - Variables
xandydeclared - vairables initialized with values
- x stores 12 and y stores 6
window.alert(x + y);- sums x and y to produce 18
- displays an alert box
- Appears as popup
- User must press OK to clear
-
question 2

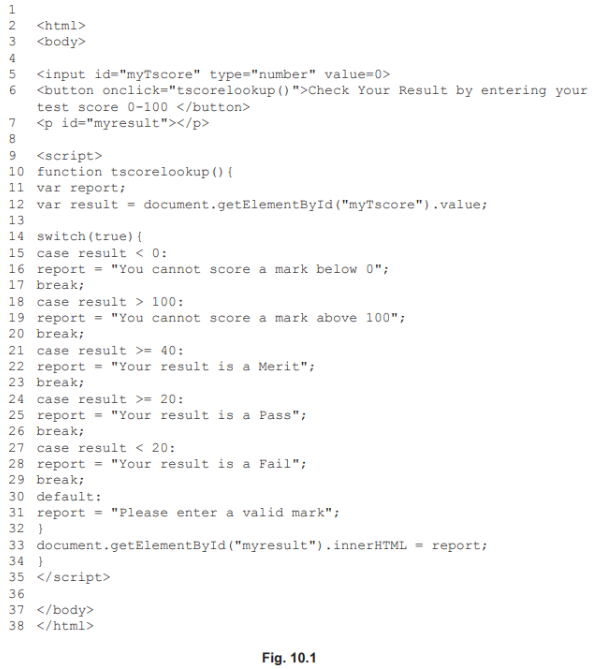

- answer
- Line 9
<script>declares the code to be JavaScript. - Line 10 declares a function called
- Line 11 declares variable report.
- Line 12 declares variable result.
- Line 12 collects value/18 of 'myTScore' from user input into HTML code at line 5 and stores it in variable 'result
- Line 14 'switch' function is used to compare the value in 'result' against pre- set 'case' values.
- Line 15 checks value of 'result' to see if condition is TRUE.
- Line 18 checks value of 'result' to see if condition is TRUE.
- Line 21 checks value of 'result' to see if condition is TRUE.
- Line 24 checks value of 'result' to see if condition is TRUE
- all of these are FALSE
- control moves to next case
- Line 27 checks value of 'result to see if condition <20 is TRUE
- this is TRUE so control passes to Line 28 and FAIL comment is stored in variable
report
- this is TRUE so control passes to Line 28 and FAIL comment is stored in variable
- Line 33 function displays contents of variable '
report' on webpage/displays "Your result is a Fail"; - '
break' is included to exit/jump out of any case - '
default' is included in case no preceding is TRUE - Including '
default' is good coding practice even if not required.
- Line 9
-
question 3

- answer
- If statement specifies block of code that is executed if a condition is TRUE
- Line 4 if statement compares 'age' with condition <10
- if TRUE 'You are not old enough...'is stored in variable 'statement'
- if FALSE execution is passed to line 6
- Else-if statement specifies a new condition to be checked if the first condition is FALSE
- Line 6 else if statement compares 'age' with condition <18
- if TRUE 'You can go to this is stored in variable 'statement'
- if FALSE execution is passed to line 8 and "You are too old to go to this school" is stored in variable 'statement'
- Else statement specifies the code to be executed if condition is FALSE.
-
question 4

- answer
- The order of Case/conditions checks in code must be logically correct/perfect
- for correct lexpected comparisons to be made
- (Switch) syntax does not follow the usual rules/colons not semi-colons so
- code is difficult/confusing to write/read
- Code can be lengthy as each condition has to be individually stated
- this is repetitive and prone to error
- 'break' has to be manually inserted after every 'case'
- debugging problems/difficulties with 'nested' conditions
- 'default' condition should be included to catch/trap unexpected conditions.
- The order of Case/conditions checks in code must be logically correct/perfect
-
question 5


- answer
- Line 4 declares the variable/var length to hold one side of rectangle
- Line 5 declares the variable/var width to hold other side of rectangle
- parseFloat (prompt("")); used to display message
- parseFloat (prompt("")); used to collect values for both sides of rectangle
- parseFloat (prompt("")); used to create a (text) box for the user to enter the values
- Variable/var calc area is declared to calculate the area
- Holds result of calculation
- document.write() is used to display the messages on screen about the
- values/area of the rectangle
- Displays the results of the calculation/contents of var calc_area.
-
question 6

- answer
- Line 7 contains a syntax error
- "Peter" is enclosed in quotes that are the same as the quotes for the string
- (Strings in JavaScript can contain quotes but) the quotes in a string must not be the same as the enclosing quotes
- Any syntax error causes the script to fail/not run
- No error message is produced.
-
question 7
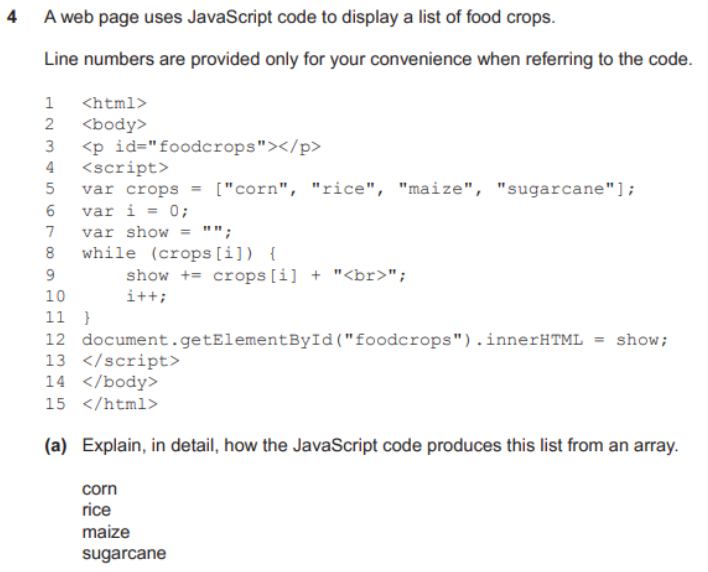
- answer
- Code is embedded in HTML code of the website by
<script>and</script>delimiters/markers - The browser executes the JavaScript code within the delimiters
- Variable crops is set to contain the list of crops
- Variables i and show are initialised
- While loop will continue looping as long as crops contains data/string
- (var) i is incremented by 1 each time loop is executed
- (var) show is set to the current value of show concatenated with next crop value
- Loop terminates when array has no more items/final value in array is reached
- Final values of (var) show are displayed on screen/web page
- Values shown in vertical list as
<br>code forces carriage return/line feed.
- Code is embedded in HTML code of the website by
-
question 8

- answer
-
question 9


- answer
<form action="mailto: aftersales@mycompany.com"- Tells the page that this is a form
- submitting form to a specified URL
- To send an email via mailto to the specified address
method="post"- Specifies the HTTP method when submitting form
- In this case post means not to display the submitted data
- is not saved in browser history
- not passed in as GET request with URL parameters
- Post can send unlimited amounts of data
- no size restrictions
enctype="text/plain"- Specifies the encoding of the data
- As plain text.

- answer

- answer
-
question 10

- answer
-
question 11

- answer
- A colon (:) is shown instead of a semi-colon (;) in line 6
- this is a syntax error
- Syntax errors prevent JavaScript from being executed
- The web browser displays nothing
- The variable 'tableout' has not been declared before it is used
- Some browsers will ignore
- Results can be different in different browsers.
- A colon (:) is shown instead of a semi-colon (;) in line 6
-
question 12

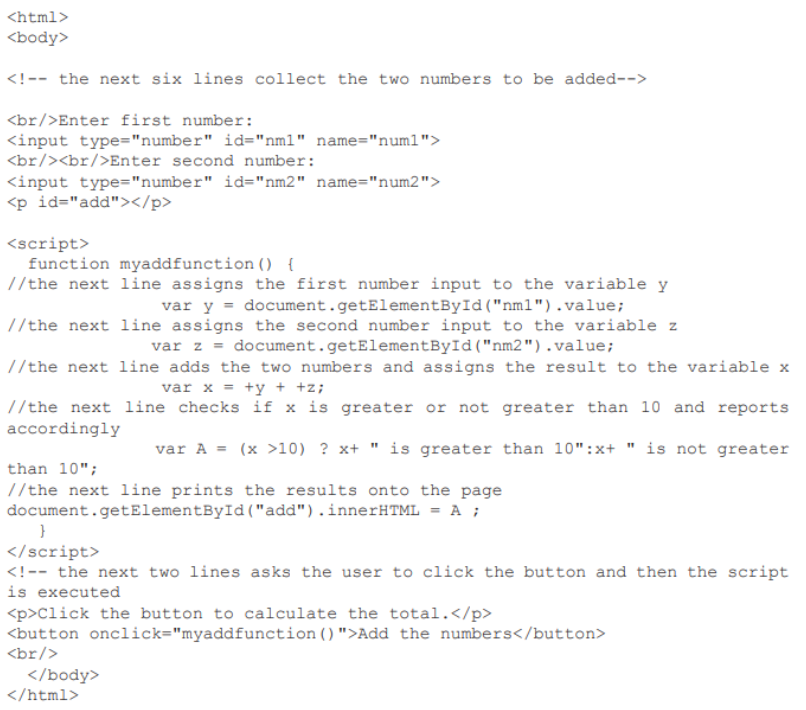

- answer (tetsing)
- Checking each line of code
- Ensures that each line of code is executed at least once
- Ensures that var y and z assign the collected numbers as required
- Checks that the additon of y and z is correct
- Ensures that the correct message is displayed when result assigned to A
- Checking each branch/decision in the code
- Checks that decisions are carried out correctly
- So that values put in A can be compared
- Ensures that result is checked against > 10
- Ensures that the correct result is put in var x as required
- Checks every possible pathway through the code
- So that test values in var y and z cause each subsequent path to be followed
- So that test values in x are assigned to A to produce both the messages "is greater than 10" and "is not greater than 10" depending on value in A.

- answer
- Can separate code into different functional
- for easy understanding, maintainance, testing
- Separating HTML and JavaScript code provides modularity to code
- Which is easier to maintain
- Can re-use the code
- No need to rewrite copies on each web page
- Code only tested once once
- JavaScript file gets cached by web browser
- No need to reload/fetch it if need on other pages
- Reduces network access cost
- JavaScript code embedded reduce browser performance
- Web page can slow down while browser executes code.
- Can separate code into different functional
-
question 13
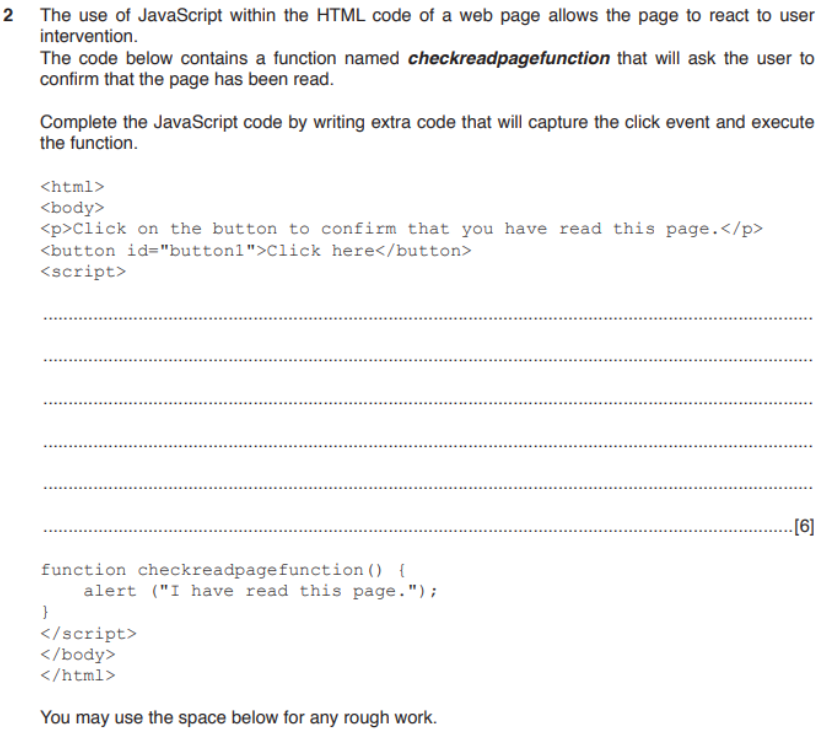
- answer
const b1 = document.getElementById("button1");
b1.addEventListener("click", checkreadpagefunction);
// its better to single-line it
document.getElementById("button1").addEventListener("click", checkreadpagefunction);
-
question 14



- answer
- Use validation to apply a format check to email address
- Ensures email has @ symbol and domain name
- Use drop-down list to select the security question
- To select date numbers from drop down lists
- range check for month/day/years allowed
- Check if date is sensible
- Use of radio buttons with Boolean choices
- Select check box for terms and conditions
- Check password for strength
- check length
- Compare the two password
- presence check ensures that all required fields are completed
- Customer visually reads form to check for possible errors
- When submit button pressed
- data is checked and validated
- before sending to the backend

- answer
- submit button
- to send data to backend
-
question 15
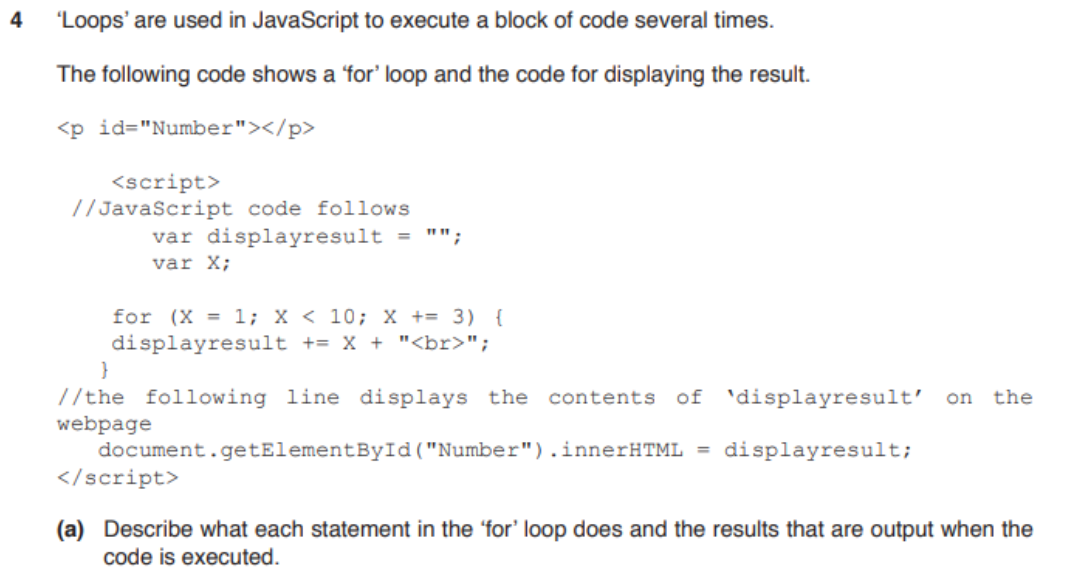
- answer
- Variables X and 'displayresult' are declared
- and cleared before use by
- Loop starts with X at 1
- X is incremented by 3 each time it
- Continues until X reaches 10/while X is less than 10
- Displays result as 1, 4, 7
- on separate lines

- answer
<p id="Number"></p>var x = 1;
const pNum = document.getElementById("Number");
do {
pNum.innerHTML += x + "<br>";
x = x + 3
// with a stepping of 3
} while (x < 10)

- answer
- The code is executed by the web browser
- Not on the web server
- Web browser may not support the code language
- So the code may not execute property/at all/produce errors
- Different browsers run code in different ways
- Developers must test all code with all browsers
- Same browsers on different operating systems behave differently
- Code may produce different results
- Code requires high processing power
- So webpages may display slowly/not at all
- Non-functioning code may deter viewers leading to loss of audience/sales
- via the website.
-
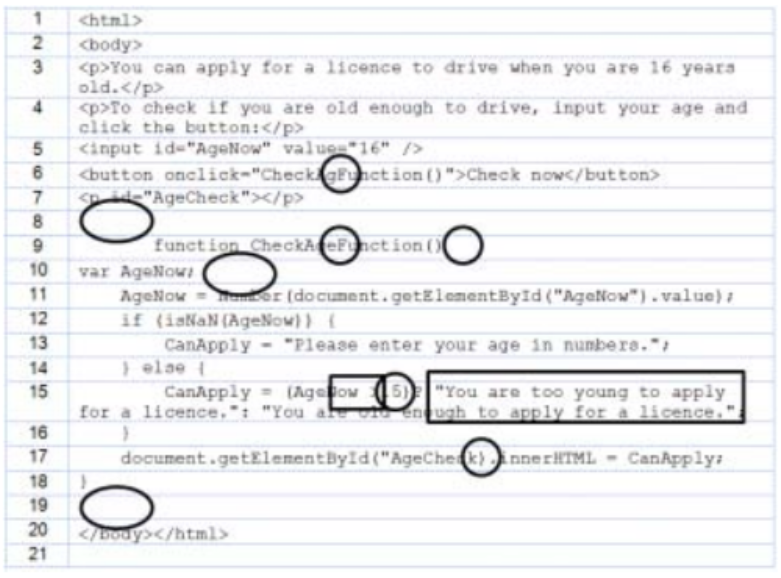
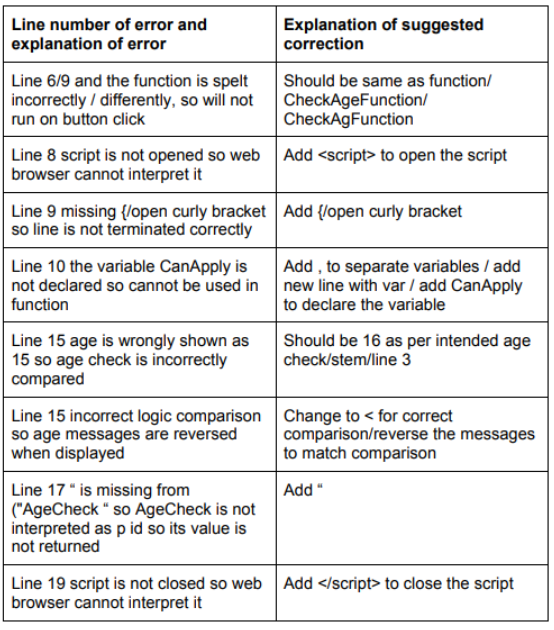
question 16
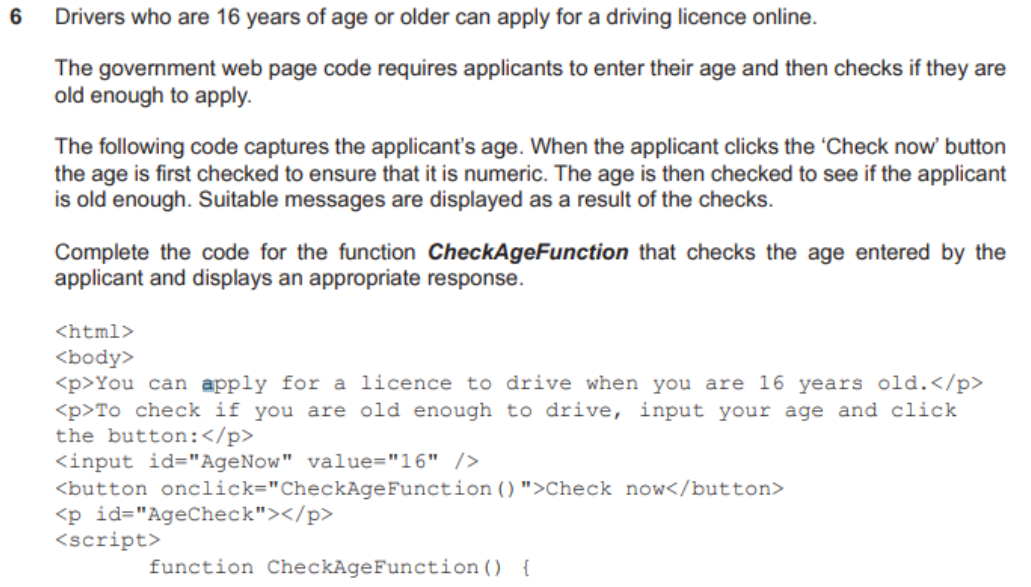

- answer
var AgeNow, CanApply;
const AgeNowElement = document.getElementById("AgeNow")
AgeNow = Number(AgeNowElement.value);
if (isNaN(AgeNow)) {
CanApply = "Please enter your age in numbers"
} else {
// using ternary operator here
CanApply = (AgeNow < 16) ? "You are too young to apply" : "You are old enough to apply"
}
-
question 17
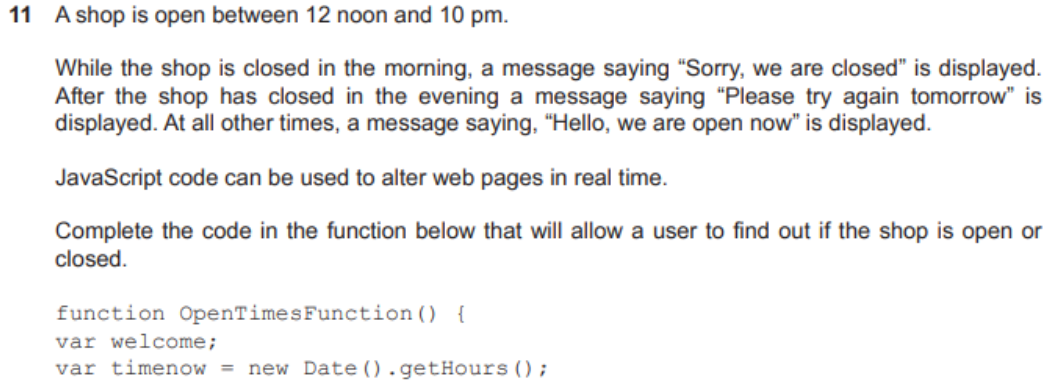

- answer
if (timenow < 12) {
welcome = "Sorry, we are closed"
}
else if (timenow < 22) {
welcome = "Hello, we are open now"
}
else {
welcome = "Please try again tommorow"
}
-
question 18
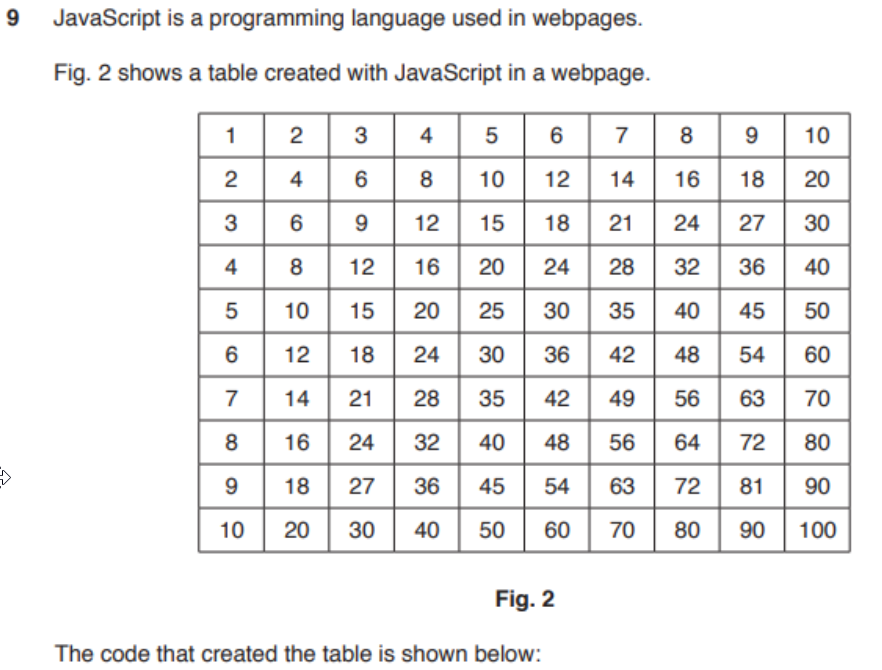


- answer
- Code is embedded to the
<body>of document - (global) variable is declared
- The HTML table values are placed within the variable
- (first) outer loop (on 4th line of JS code) executes 10 times
- to create each row (using
<tr>) - (Second) inner loop is executed each time outer loop executes
- to create 10 columns
- First time inner loop executes, the cell contains 1+1=1
- second time inner loop executes, the cell contains 1 *2=2
- third time inner loop executes, the cell contains 1+3=3
- up to cell that contains 1* 10=10
- When inner loop reaches 10, first row of cells is complete...
- next row is started with ? 1=2, etc.
- up to 2'10=20
- The process continues until outer loop reaches 10
- and all 10 rows have been created and filled.
- Code is embedded to the
Other
-
why javascript uses browser to display results?
- lacks capability for displaying output
-
how JS interacts with user?
- code required to collect user data/input
- confirm(), prompt() to enable user interaction
- code places within HTML web page
- code stored in external scripts invoke when called
CSS
Colors
- More about RGB, CMYK in Chapter 9 - Graphics
- HSL (Hue-Saturation-Luminence)
- syntax:
hsl()used in CSS - to specify a color
- creates gradients of colors from the RGB model
- Hue
- value/degree on standard color wheel
- from 0 to 360
- 0: red
- 120: gren
- 240: blue
- is brightness
- how much white is added to a color
- Saturation
- intensity of color
- from grey to full color
- is a percentage
- must include
%characters
- must include
- intensity of color
- Lightness / Luminence
- from black to white
- is a percentage
- must include
%characters
- must include
- syntax: